TL;DR:
- Moonware’s HALO is an AI-powered OS for ground operations in aviation.
- HALO algorithmically coordinates ground activities in real-time, reducing delays and congestion.
- The software mines real-time flight data, crew schedules, and precise ground positions.
- Moonware secures $2.5 million in funding from prominent investors.
- HALO’s autonomy ambitions include integrating AI in various ground operation aspects.
- Moonware plans to launch with commercial airlines, starting in Europe, with potential U.S. Air Force collaboration.
- HALO aims to streamline ground operations at major airline hubs, leading to increased flight capacity without extra costs.
Main AI News:
In the fast-paced world of aviation, ensuring on-time departures is nothing short of a miracle. Behind the scenes, an intricate dance of coordination takes place, involving countless data points and a substantial ground workforce. Often overlooked by passengers, ground support crews play a pivotal role in loading catering and baggage, refueling planes, and assisting in taxiing.
However, the current state of ground operations is far from optimal, with CEO Javier Vidal of Moonware, a Los Angeles-based startup, calling it “manual and uncoordinated.” Walkie talkies and papers still dominate the scene, leading to last-minute scrambles to find the right people and equipment to service flights on time.
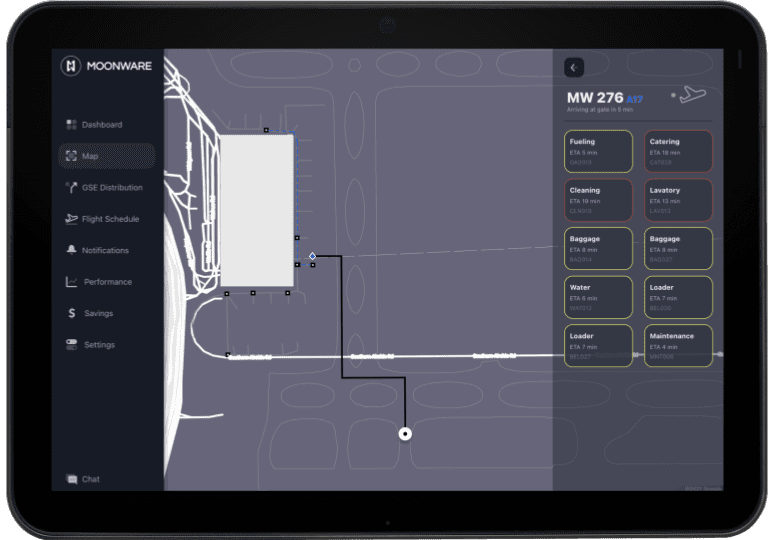
Moonware has a bold solution to this predicament – an AI-powered Operating System (OS) for ground operations, aptly named HALO. This innovative software leverages algorithms to coordinate ground activities in real-time. By considering variables like distance, departure and arrival times, and crew availability, HALO automatically dispatches crews and equipment, promising to reduce delays, airfield congestion, and plane turnaround time.
The brilliance of HALO lies in its ability to mine three essential data streams: real-time flight information, crew schedules, task allocation, and precise ground positions and movements. This proprietary data stream, exclusive to Moonware, relies on work cell phones and low-cost GPS trackers to collate the locations of all the elements in the airfield workflow.
Drawing parallels to air traffic control (ATC), Moonware’s HALO functions as a ground traffic control platform, proving adaptable to various airfield environments, including commercial airlines, cargo carriers, defense, and eventually eVTOL operators.
Investors have taken notice of Moonware’s cutting-edge solution, with the startup recently securing $2.5 million in pre-seed financing, led by early-stage VC firm Third Prime, along with support from Zero Infinity Partners, The House Fund, Lorimer Ventures, Plug and Play, and several angel investors.
However, Moonware’s ambitions go beyond software. The company envisions a future where autonomy is woven into every aspect of ground operations, from baggage transport vehicles to pushback tractors that guide aircraft to the runway.
Moonware’s phased approach begins with the launch of the HALO OS with commercial airlines, starting with those that manage their ground operations team, such as Delta Airlines hub in Atlanta or United at SFO. Fortunately, the areas of ground operations fall outside the strict regulatory purview of the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration, allowing Moonware to launch and scale swiftly.
The company’s inaugural deployment will be with a major European carrier, with plans to service around ten flights daily, eventually scaling up to 15 to 20 flights over four to 6 months.
Moonware aspires to expand vertically across major airline hub airports, anticipating a network effect as more hubs embrace HALO. As time savings compound, airlines can increase their daily flight capacity without additional aircraft purchases, thereby optimizing efficiency and reducing capital expenditures.
Beyond commercial aviation, Moonware is also in discussions with the U.S. Air Force, which grapples with similar ground operations coordination challenges. The potential introduction of autonomy in the coming decade will be particularly beneficial as new forms of transportation, like eVTOL and commercial hypersonic flight, take center stage.
With airports becoming multi-modal hubs, Moonware sees HALO as the critical ecosystem to manage diverse aircraft servicing needs efficiently, ensuring compatibility and streamlined operations.
Conclusion:
Moonware’s HALO represents a significant advancement in the aviation market. By leveraging AI to coordinate ground operations in real-time, HALO addresses long-standing challenges in the industry, such as delays and airfield congestion. Its successful funding round demonstrates strong investor interest and confidence in the technology’s potential. As Moonware expands its reach, partnering with major airlines and exploring opportunities with the U.S. Air Force, HALO has the potential to become the standard solution for optimizing ground operations worldwide. Airlines and aviation authorities can expect increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved passenger experiences, making HALO a transformative force in the market.