TL;DR:
- AI hardware advancements are shaping industries like robotics, smart homes, and autonomous vehicles.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) introduces AWS Inferentia, a custom machine learning inference chip, while Colossus MK2 IPU processor accelerates AI with a novel approach.
- IBM Research pioneers analog in-memory computing (analog AI) to enhance deep learning reasoning.
- Analog AI faces challenges of computational accuracy and integration with digital systems.
- IBM Research’s mixed-signal analog AI hardware marks a significant step forward in energy-efficient AI.
- Analog in-memory computing (AIMC) reduces energy consumption in deep neural network inference tasks.
- AIMC’s success hinges on on-chip digital processes and communication enhancements.
- IBM’s multicore AIMC chip achieves impressive precision in image recognition tasks.
Main AI News:
In the ever-evolving landscape of artificial intelligence (AI), the demand for specialized hardware has surged, with applications ranging from robotics and smart homes to autonomous vehicles. This transformation, often referred to as the LLM (Machine Learning and Deep Learning) revolution, has spurred the development of cutting-edge AI chips designed to enhance the performance of deep learning applications in the cloud.
One notable player in this arena is Amazon Web Services (AWS), which has introduced a game-changing innovation known as AWS Inferentia. This custom machine learning inference chip is poised to redefine the AI landscape. Additionally, the Colossus MK2 IPU processor, developed in conjunction with the Poplar SDK, promises to accelerate AI applications with its novel approach to massively parallel processing.
IBM Research Takes a Leap Forward
In tandem with these developments, IBM Research has entered the fray with its groundbreaking AI chip, designed to bolster deep learning reasoning. This innovative venture aims to rethink AI’s computational foundations, exploring the realm of analog in-memory computing, often referred to as “analog AI.” The premise behind analog AI is grounded in emulating the synaptic strengths that govern neural connections within the human brain and the brains of other living organisms.
The Analog AI Implementation Challenge
The implementation of analog AI presents formidable challenges. It demands data stores capable of achieving computational accuracy on par with current digital systems, all while seamlessly integrating with the digital components of AI chips. These chips must also communicate effortlessly with digital communication networks.
A Breakthrough in Mixed-Signal Analog AI Hardware
IBM Research has published a groundbreaking study introducing state-of-the-art mixed-signal analog AI hardware. This innovation represents a significant stride toward overcoming the hurdles posed by analog AI implementation. Notably, this analog chip achieves the same level of efficacy in computer vision AI tasks as its digital counterparts while offering substantial gains in energy efficiency.
Unlocking Efficiency with Analog In-Memory Computing (AIMC)
The study elucidates how AIMC can dramatically reduce AI computing energy consumption. By performing computations directly within memory and harnessing resistive memory devices, AIMC mitigates latency and energy consumption in deep neural network inference tasks. However, achieving optimal results requires coupling AIMC with on-chip digital processes and on-chip communication, further enhancing latency and energy utilization.
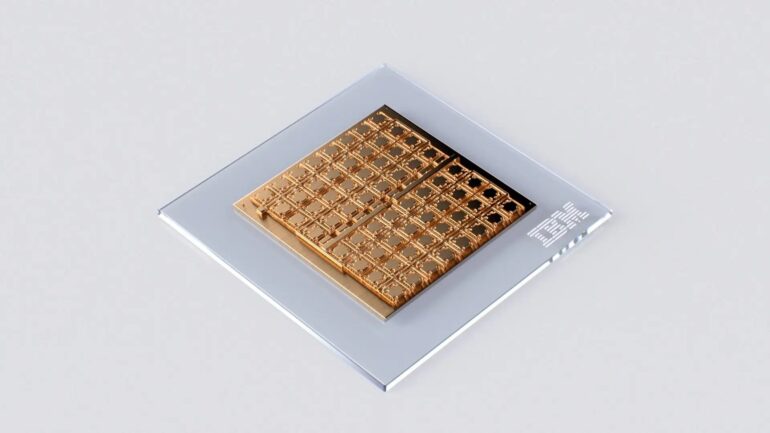
Multicore AIMC Chip: A Marvel of Integration
IBM’s state-of-the-art chip, manufactured at the Albany NanoTech Complex, boasts 64 analog in-memory compute cores or tiles. Each tile features a 256-by-256 crossbar grid of synaptic unit cells and incorporates a sophisticated analog-to-digital translator to seamlessly bridge the analog and digital realms. Furthermore, these tiles incorporate digital processing units capable of executing nonlinear neural activation functions and scaling operations.
In a remarkable demonstration of its capabilities, IBM’s chip achieved an impressive precision rate of 92.81% on the CIFAR-10 picture dataset. This achievement stands as a testament to the chip’s accuracy and marks a significant milestone in the pursuit of analog in-memory computing excellence.
Conclusion:
The advancements in AI hardware, particularly in the realm of analog AI, represent a significant leap forward for the market. These innovations promise to drive greater efficiency, energy savings, and computational power in AI applications, thereby opening up new possibilities across industries such as robotics, smart homes, and autonomous vehicles. Companies like AWS and IBM are at the forefront of shaping the AI hardware landscape, with potentially far-reaching implications for the global economy.