TL;DR:
- Recent developments enhance synthesized speech in text-to-speech systems.
- Voice variability remains a challenge in TTS.
- Microsoft introduces PromptTTS 2 to address voice variability.
- It uses text prompts and a variation network for better voice modeling.
- Automated prompt creation reduces dependency on vendors.
- PromptTTS 2 outperforms previous studies in voice quality and variability control.
Main AI News:
Recent strides in the world of text-to-speech (TTS) technology have propelled synthesized speech toward unprecedented levels of intelligibility and naturalness. The emergence of large-scale TTS systems designed for multi-speaker environments has been a defining milestone. In fact, some TTS systems have reached a level of quality that rivals single-speaker recordings. Nevertheless, despite these remarkable advancements, the challenge of modeling voice variability persists.
Voice variability plays a pivotal role in communication, allowing us to convey emotions, tone, and subtle nuances in our speech. Traditional TTS techniques have often relied on predefined speaker information or speech prompts to emulate voice variability. Unfortunately, these methods fall short of being user-friendly. The constraints of pre-defined speaker identification and the quest for suitable speech prompts hinder the seamless integration of voice variety into synthesized speech.
A more promising avenue for addressing voice variability lies in the realm of text prompts. By utilizing text prompts that specify voice features, we can tap into the richness of natural language to empower users to craft their desired voices. These text prompt-based TTS systems are trained on datasets of speech paired with corresponding text prompts, with the text prompts serving as guides for generating nuanced voices.
Yet, challenges persist in the world of text prompt-based TTS systems:
- One-to-Many Challenge: The variability of voice quality among individuals poses a significant hurdle. Written instructions struggle to capture all the intricacies of speech, leading to different voice samples correlating with the same prompt. This one-to-many phenomenon complicates TTS model training, risking overfitting or mode collapse. Remarkably, there have been no dedicated procedures to tackle this challenge—until now.
- Data-Scale Challenge: Compiling datasets of text prompts that define voice characteristics is no easy feat. Typically, vendors are hired to create such prompts, a process both costly and time-consuming. These prompt datasets are often limited in size or remain private, hampering further research in the domain of prompt-based TTS systems.
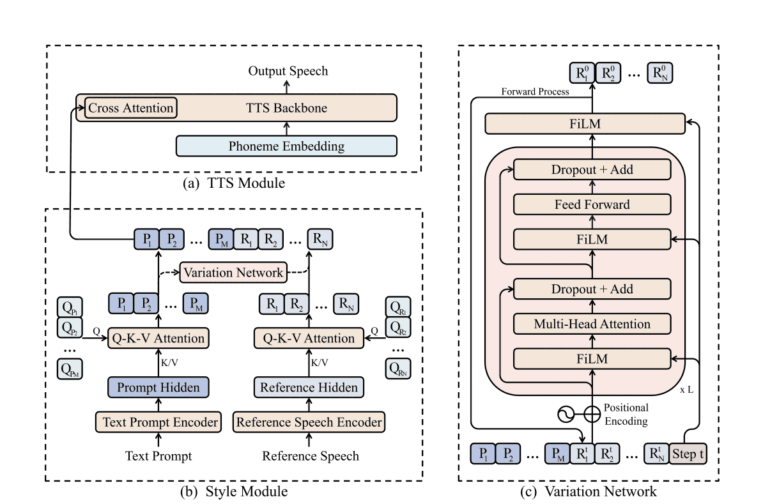
In response to these challenges, the team at Microsoft presents PromptTTS 2, a groundbreaking solution that introduces a variation network to capture voice variability information not covered by the prompts themselves. This ingenious approach harnesses the capabilities of large language models to generate high-quality prompts, thus surmounting the aforementioned obstacles. The variation network anticipates missing voice variability information from the text prompt for the one-to-many challenge, with reference speech serving as the training foundation.
The TTS model in PromptTTS 2 consists of a text prompt encoder, a reference speech encoder, and a TTS module. Together, these components synthesize speech based on the representations retrieved by the text prompt encoder and reference speech encoder. The variation network, trained using the immediate representation from the text prompt encoder, predicts the reference representation from the reference voice encoder. This innovative model empowers users to modify the qualities of synthesized speech using the diffusion model within the variation network, offering unprecedented freedom in voice production.
Moreover, Microsoft’s researchers propose an automated pipeline for creating text prompts for speech. This pipeline employs a speech understanding model to extract voice characteristics from speech samples, and a massive language model constructs text prompts based on these attributes. Unlike previous methods that relied on manual phrase construction by vendors, PromptTTS 2 leverages the capabilities of large language models, capable of performing tasks at a human level. This entirely automated workflow eliminates the need for human intervention in prompt authoring.
Conclusion:
Microsoft’s PromptTTS 2 represents a significant advancement in the TTS market. Addressing the challenges of voice variability modeling and automating prompt creation not only enhances the quality of synthesized speech but also reduces reliance on external prompt providers. This innovation sets a new standard, offering businesses and users more control over voice production and paving the way for more natural and customizable voice synthesis solutions in various industries.