TL;DR:
- Image-to-image translation (I2I) is a cutting-edge technology that transforms visuals across domains.
- Revive-2I, an innovative I2I approach, tackles the challenge of translating skulls into living animals (Skull2Animal).
- Revive-2I utilizes text prompts for precise transformations and offers realistic results.
- It employs natural language prompts for zero-shot I2I via latent diffusion models.
- Revive-2I’s process involves encoding, diffusion, and text-guided decoding for faster and more efficient translations.
- Experimentation with partial steps in diffusion preserves source image content while integrating target domain features.
- Applications include aiding law enforcement in suspect identification, illustrating climate change’s impact on ecosystems, and bringing ancient fossils to life.
Main AI News:
Image-to-image translation (I2I) stands at the forefront of computer vision and machine learning, offering the remarkable ability to seamlessly transform visual content from one domain into another. This groundbreaking process transcends mere pixel manipulation; it hinges upon a deep comprehension of underlying structures, semantics, and style nuances within images.
I2I has permeated diverse domains, from crafting artistic renditions of photographs to transmuting satellite imagery into maps and even transcribing sketches into photorealistic portrayals. The driving force behind this transformative technology lies in the prowess of deep learning models, notably Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs).
Traditionally, I2I methods have been fixated on bridging relatively narrow gaps between domains, such as converting photos into paintings or morphing distinct animal species. These tasks, while challenging in their own right, do not necessitate the creation of substantially new visual attributes or structural inferences during the translation process.
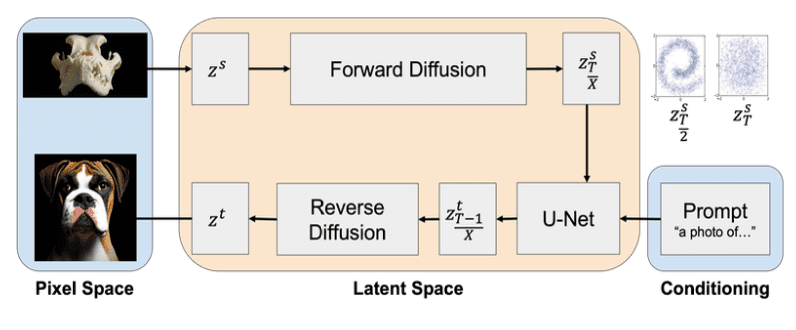
Enter Revive-2I, a pioneering approach within the I2I realm that embarks on the ambitious journey of translating skulls into living, breathing animals, aptly named Skull2Animal.
Skull2Animal represents a formidable challenge as it involves metamorphosing lifeless skulls into vibrant, living creatures. This task demands the generation of novel visual features, textures, colors, and intricate geometric inferences specific to the target domain.
Revive-2I takes an ingenious approach to tackle the intricacies of protracted I2I translations by leveraging text prompts to articulate the desired image transformations. This methodology ensures the production of realistic and verifiable results, raising the bar for acceptable translations and ensuring fidelity to the intended target domain.
At the heart of Revive-2I lies the use of natural language prompts to execute zero-shot I2I via latent diffusion models.
Revive-2I comprises two pivotal stages: encoding and text-guided decoding. In the encoding phase, the source image undergoes transformation into a latent representation through a process called diffusion. This latent representation is subsequently injected with noise to facilitate the incorporation of desired alterations. By conducting the diffusion process within the latent space, Revive-2I achieves not only swifter but also more resource-efficient translations.
Discovering the optimal balance for Revive-2I was a journey fraught with challenges. It necessitated experimentation with varying numbers of steps in the forward diffusion process. Partial steps emerged as a breakthrough, enabling the translation process to delicately preserve the source image’s core while seamlessly integrating features characteristic of the target domain. This approach empowers more robust translations, all while staying true to the transformative potential of text prompts.
The ability to execute constrained, protracted I2I translations carries profound implications across a multitude of domains. Law enforcement agencies can harness this technology to generate lifelike suspect images from sketches, greatly aiding in the identification process. Wildlife conservationists gain the ability to vividly showcase the impact of climate change on ecosystems and habitats by transmuting images of endangered species into their living counterparts. Additionally, paleontologists can now breathe life into ancient fossils, rendering them as images of their once-thriving, prehistoric forms. It seems that the dream of creating our very own Jurassic Park is closer than ever to becoming a reality.
Source: Marktechpost Media Inc.
Conclusion:
The emergence of Revive-2I signifies a breakthrough in image-to-image translation technology, opening doors to precise, real-world applications across various sectors. Its ability to translate skulls into living animals, driven by text prompts and diffusion models, has significant implications for law enforcement, conservation efforts, and paleontology, creating new opportunities and efficiencies in these markets.

