TL;DR:
- UCI and Harvard researchers introduced TalkToModel, an interactive dialog system for explaining machine learning models.
- TalkToModel aims to address the opacity of complex AI models and boost trust among users.
- It comprises three key components: a dialog engine, an execution unit, and a conversational interface.
- Testing shows promising results, with healthcare workers and machine learning developers expressing enthusiasm.
- TalkToModel could enhance AI comprehension and trust, potentially reaching a wider audience.
Main AI News:
In today’s fast-paced world, machine learning models have become the backbone of innovation, powering everything from cutting-edge smartphones to indispensable software packages and online services. Yet, their inner workings have remained shrouded in complexity, often leaving even seasoned computer scientists scratching their heads.
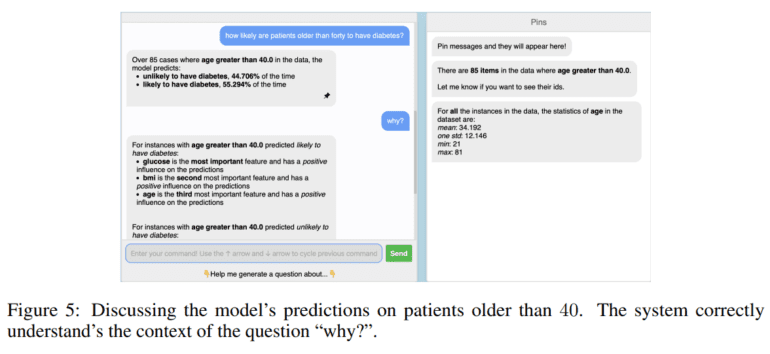
Enter TalkToModel, a groundbreaking initiative brought to life by the collaborative efforts of researchers from the University of California-Irvine and Harvard University. TalkToModel is not just another Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) tool—it’s a game-changer. This interactive dialogue system is designed to demystify machine learning models and their predictions, catering to both experts and those without a technical background.
The existing landscape of XAI tools has its limitations, often providing explanations that leave room for interpretation. TalkToModel rises above these challenges, offering users clear and pertinent insights into AI models and their inner workings. The system comprises three integral components: an adaptive dialogue engine, an execution unit, and a user-friendly conversational interface. The dialogue engine interprets natural language input, delivering coherent responses. The execution component crafts AI explanations, which are then translated into accessible language for users. The conversational interface acts as the bridge through which users engage with the system.
TalkToModel’s effectiveness was put to the test, with professionals and students offering their feedback. The results were overwhelmingly positive, with a majority of participants hailing the system as both useful and engaging. Notably, 73% of healthcare professionals expressed their eagerness to embrace TalkToModel as a means to gain insights into the predictions of AI-based diagnostic tools. Moreover, a staggering 85% of machine learning developers found TalkToModel to be far more user-friendly than other XAI tools currently available.
This encouraging feedback underscores TalkToModel’s potential to enhance comprehension and trust in AI predictions. As this platform continues to evolve, it holds the promise of being made accessible to a broader audience, contributing significantly to the ongoing mission of demystifying AI and reinforcing confidence in its capabilities. By facilitating open-ended conversations with machine learning models, TalkToModel represents a remarkable stride towards making advanced AI systems more approachable and comprehensible for all.
Conclusion:
The introduction of TalkToModel signifies a significant step forward in the AI market. This innovative tool has the potential to not only enhance understanding and trust in AI predictions but also make advanced AI systems more accessible to a broader audience. As industries increasingly rely on AI technologies, TalkToModel’s ability to bridge the gap in AI understanding could drive greater adoption and utilization of these powerful tools, fostering innovation and growth in the market.