TL;DR:
- Generative AI is gaining momentum and is compared to the transformative impact of the internet.
- Executives recognize its potential but are cautious in deployment due to understanding risks.
- Collaboration with startups and Big Tech is key for successful scaling.
- Generative AI is democratized across companies of all sizes, boosting smaller businesses.
- Workforce reduction is expected, but demand for skills in AI-related fields is rising.
- Regulatory uncertainty remains a primary challenge, with the government facing the highest level.
Main AI News:
In the wake of overhyped tech trends like Web3, the metaverse, and blockchain, business executives are now bracing for the impending tidal wave of generative AI. Some liken this shift to the transformative impact of the internet or the advent of the desktop computer. However, this surge in generative AI power is accompanied by a commensurate surge in responsibility, as it brings not only opportunities but also substantial risks. This technology is currently testing the boundaries of legal regimes concerning copyright and intellectual property. It is also giving rise to new cyber and data governance threats, while simultaneously fueling anxiety about automation in the workforce.
In this evolving landscape, organizations find themselves in a race to meet stakeholder expectations. Yet, they must proceed with utmost caution to ensure they stay within the boundaries of regulations and ethical standards, particularly in areas like data privacy and bias mitigation. Operationally, enterprises are forced to reconfigure their workforces and establish strategic partnerships with technology companies. These steps are essential to design, develop, and deploy generative AI solutions that are not only innovative but also safe, effective, and reliable.
To gain insights into the strategies and considerations of business leaders at this pivotal juncture, MIT Technology Review Insights conducted a comprehensive survey. This survey involved 1,000 executives and covered aspects such as current and anticipated use cases for generative AI, implementation challenges, technology strategies, and workforce planning. Additionally, expert interviews were conducted to complement the survey findings, offering a comprehensive view of the major decisions facing executives.
Key Takeaways from the Survey and Expert Interviews:
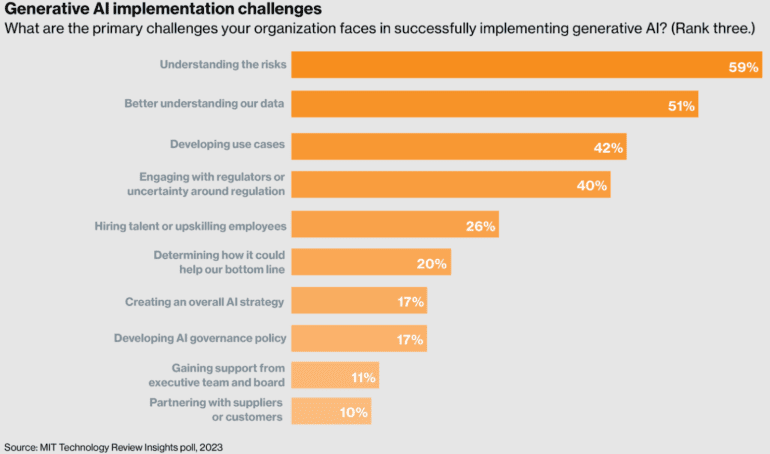
- Transformational Potential: Executives acknowledge the transformative potential of generative AI, but they are proceeding cautiously with deployment. Nearly all surveyed firms believe that generative AI will impact their business in some way, with only a minuscule 4% asserting it won’t affect them. However, at this juncture, a mere 9% have fully deployed generative AI use cases within their organizations. Interestingly, this figure drops to just 2% in the government sector, while financial services (17%) and IT (28%) lead in adoption. The primary obstacle hindering wider deployment is the understanding of generative AI risks, identified as a top-three challenge by 59% of respondents.
- Collaborative Approach: Companies are recognizing that they can’t navigate this terrain alone. Collaborations with both startups and Big Tech will be pivotal to the successful scaling of generative AI. A significant 75% of executives plan to work with partners to implement generative AI at scale, and only a small minority (10%) consider partnering as a major implementation challenge. This suggests the presence of a robust ecosystem of providers and services available for collaborative efforts. While Big Tech giants have an advantage as developers of generative AI models, startups possess unique strengths in specialized niches. Executives are slightly more inclined to partner with small AI-focused companies (43%) than with large tech firms (32%).
- Democratization of Access: The democratization of generative AI is not confined to company size. The survey found that company size does not determine a firm’s likelihood to experiment with generative AI. In fact, small companies (with annual revenue less than $500 million) are three times more likely than mid-sized firms ($500 million to $1 billion) to have deployed generative AI use cases (13% versus 4%). These smaller enterprises exhibit deployment and experimentation rates akin to those of the largest companies (with revenue exceeding $10 billion). Affordable generative AI tools hold the promise of leveling the playing field for smaller businesses, akin to the transformative impact of cloud computing.
- Workforce Dynamics: Approximately one-quarter of respondents anticipate that generative AI will lead to a reduction in their workforce. This figure is higher in industrial sectors such as energy and utilities (43%), manufacturing (34%), and transport and logistics (31%). Conversely, it is lowest in the IT and telecommunications sector (7%). However, this overall reduction is relatively modest when compared to more dire job replacement scenarios. The demand for skills in operationalizing AI models and addressing ethical and risk-related challenges is on the rise. AI is democratizing technical skills across the workforce, potentially creating new job opportunities and enhancing employee satisfaction. Nevertheless, experts caution that if generative AI deployment lacks meaningful consultation and is executed poorly, it could diminish the quality of the human work experience.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: While regulation is looming on the horizon, uncertainty remains the foremost challenge today. Generative AI has prompted a flurry of legislative activity as policymakers attempt to comprehend and mitigate associated risks. However, truly impactful regulation is expected to move at the pace of government, which can be slow. In the interim, a significant portion of business leaders (40%) cite engagement with regulation or regulatory uncertainty as a primary challenge in adopting generative AI. This challenge varies considerably by industry, with the government facing the highest level of uncertainty (54%) and IT and telecommunications experiencing the lowest (20%).
Conclusion:
The ascent of generative AI presents an array of opportunities and challenges for businesses. Success will require careful navigation, strategic partnerships, and a keen awareness of evolving regulations. As businesses contemplate their generative AI strategies, the insights gathered from this survey and expert interviews serve as valuable guideposts for making informed decisions and charting a course toward a future where generative AI is an integral part of organizational success.