TL;DR:
- NVIDIA’s Eureka AI agent can teach robots complex skills, including pen spinning, on par with humans.
- NVIDIA, known for its GPUs, also focuses on the development platform Omniverse, which includes the Voyager AI agent.
- Eureka uses generative AI and GPT-4 LLM for reinforcement learning without task-specific prompting.
- The AI’s library of algorithms is compatible with Isaac Gym, enhancing training efficiency.
- Eureka’s performance surpasses human-generated rewards in over 80% of tasks, with a 50% performance boost in robots.
- This innovation signifies a significant leap in AI-driven robotics and reinforcement learning.
Main AI News:
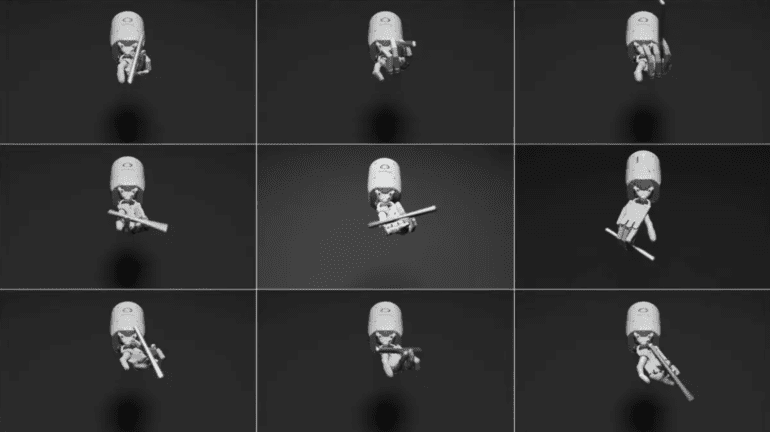
In a remarkable feat of artificial intelligence advancement, NVIDIA, a leading chipmaker, has unveiled Eureka, an AI agent capable of teaching robots intricate skills on par with human capabilities. The breakthrough announcement came through a press release, highlighting Eureka’s proficiency in tasks that include the rapid spinning of a pen, among 30 other complex undertakings, all made possible through the power of artificial intelligence.
NVIDIA, renowned for its Graphics Processing Units (GPUs), which played a pivotal role in the development of ChatGPT, has continued to push the boundaries of AI technology. The company has ventured into the realm of 3D tools and applications with its development platform, Omniverse. Earlier this year, NVIDIA introduced the Voyager AI agent, designed to construct tools at a staggering 15 times the speed of other AI agents within the Minecraft universe.
The Voyager AI agent owes its capabilities to the formidable Large Language Model (LLM) GPT-4. Building on this success, NVIDIA’s team has harnessed the same model to create an agent that can mimic complex skills at a level comparable to humans.
How does Eureka operate?
Reinforcement Learning (RL) has been a cornerstone of AI development for several years, yielding impressive accomplishments. Nevertheless, challenges persist, with reward design being a particularly vexing issue, often requiring trial-and-error approaches. Anima Anandkumar, Senior Director of AI Research at NVIDIA, elaborated on this in the press release.
Eureka represents a leap forward by integrating generative AI to craft software code that rewards robots through reinforcement learning. This is achieved using the GPT-4 LLM, eliminating the need for task-specific prompting or predefined templates. Furthermore, Eureka can adapt to human feedback, allowing for reward modification to enhance results.
Eureka’s library of algorithms finds practical application in Isaac Gym, NVIDIA’s physics simulations reference application, built on Omniverse and dedicated to reinforcement learning research. With the computational prowess of NVIDIA’s GPUs, Isaac Gym can rapidly evaluate extensive batches of reward candidates, significantly enhancing training efficiency.
The AI agent then generates a summary, which is fed into the LLM to refine reward functions using critical statistics gleaned from training outcomes. This approach is versatile, accommodating a wide range of robot types, including quadrupeds, bipeds, and quadrotors, with dexterous hands or cobot arms.
Assessing Eureka’s Performance
Beyond pen spinning, NVIDIA researchers have successfully trained robots to excel in diverse complex tasks, such as opening cabinets, tossing and catching balls, and manipulating scissors. A research paper authored by the NVIDIA team reveals that Eureka-generated rewards outperformed those written by humans in over 80 percent of the tasks performed, leading to more than a 50 percent improvement in robot performance.
The paper also details performance enhancements from in-depth evaluations involving 20 tasks where robots were trained using Eureka, showcasing their prowess in mastering complex manipulation skills.
NVIDIA is poised to inspire developers to embark on more ambitious and demanding projects, confident that Eureka will pave the way for precise robot control and revolutionize the creation of physically realistic animations, as stated by Jim Fan, Senior Research Scientist at NVIDIA, and a key contributor to this groundbreaking research.
Conclusion:
NVIDIA’s Eureka AI breakthrough is a game-changer for the robotics market. It empowers robots with human-like skills, opening doors for more sophisticated applications in various industries, from manufacturing to entertainment and beyond. This advancement demonstrates NVIDIA’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of AI technology, making it a driving force in the evolving robotics landscape.