TL;DR:
- Google introduced an advanced grammar correction feature powered by EdiT5 in its search engine.
- EdiT5 reimagines grammatical error correction as a text editing problem, reducing decoding steps and minimizing latency.
- The model employs an encoder to determine tokens to keep or delete, resulting in a draft output that is later refined by a decoder for grammatical correctness.
- Streamlined decoder and enhanced encoder size contribute to a remarkable mean latency of just 4.1 milliseconds.
- EdiT5 outperforms traditional models with higher correction accuracy and an impressive 9x speedup.
- Model size plays a crucial role in precise grammatical corrections, combining large language models with low latency through hard distillation.
- Refinement of training data eliminates unnecessary paraphrasing and grammatical errors, resulting in cleaner datasets.
- The implementation includes both a grammatical error correction model and a grammaticality classifier, ensuring accurate user suggestions.
- Google’s EdiT5-powered grammar correction sets a new industry standard for efficient and accurate grammar correction, enhancing user experience and search result reliability.
Main AI News:
In an unprecedented leap forward, Google has unveiled a cutting-edge grammar correction feature within its search engine, driven by the revolutionary EdiT5 model. This transformative innovation tackles the intricate realm of grammatical error correction (GEC) with a laser-focused approach, ensuring a blend of accuracy, efficiency, and rapidity that sets it apart from conventional methods.
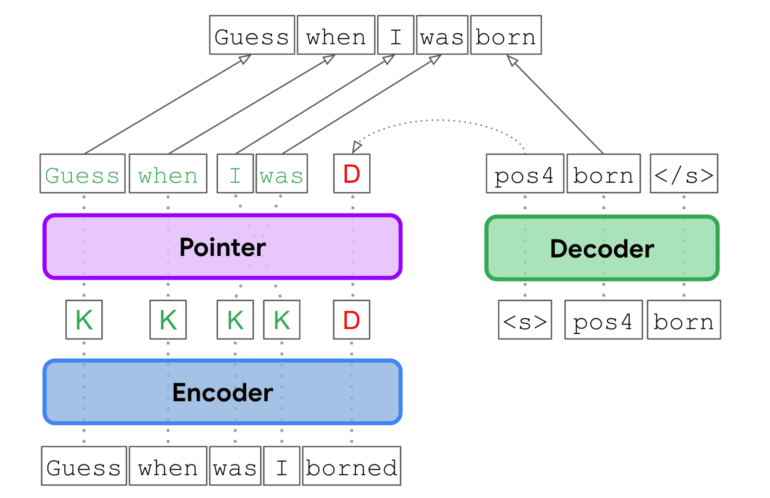
Traditionally, GEC has been approached as a translation challenge, relying on autoregressive Transformer models. While effective, this approach encounters limitations in parallelization due to autoregressive decoding. Recognizing the need for a more streamlined process, the EdiT5 team has reimagined GEC as a text editing endeavor. By harnessing the power of the T5 Transformer encoder-decoder architecture, they’ve significantly reduced decoding steps, thereby minimizing latency.
The EdiT5 model takes input laden with grammatical errors and employs an encoder to discern which tokens to retain or eliminate. These retained tokens form the foundation of a draft output, which can be optionally reordered using a non-autoregressive pointer network. Subsequently, a decoder swoops in to insert any missing tokens necessary to generate a grammatically correct output. Importantly, the decoder operates solely on tokens absent in the draft, resulting in a substantial reduction in processing time compared to the traditional translation-based GEC.
To further enhance decoding speed, the team streamlined the decoder to a single layer while bolstering the encoder’s size. This astute adjustment effectively balances the computational load and yields a significant reduction in latency. In practical terms, this translates to the EdiT5 model delivering outstanding results with a remarkably low mean latency of just 4.1 milliseconds.
Performance evaluations conducted on the public BEA grammatical error correction benchmark underscore the undeniable superiority of EdiT5. A large EdiT5 model boasting 391 million parameters outshines a T5 base model with 248 million parameters, yielding superior F0.5 scores, which serve as a metric for correction accuracy. This remarkable improvement comes paired with an astounding 9x speedup, showcasing the model’s extraordinary efficiency.
Moreover, the study accentuates the pivotal role of model size in generating precise grammatical corrections. Leveraging a technique known as hard distillation, the team masterfully combines the advantages of large language models (LLMs) with EdiT5’s low latency. Through the training of a teacher LLM and its utilization in generating training data for the student EdiT5 model, they’ve orchestrated a potent fusion of accuracy and speed.
The development journey also encompassed the meticulous refinement of training data to ensure peak performance. Training datasets, composed of ungrammatical source sentences and their grammatical target counterparts, underwent rigorous self-training and iterative refinement. This painstaking approach effectively purged unnecessary paraphrasing, artifacts, and grammatical errors, yielding cleaner and more consistent training data.
In its final iteration, the EdiT5-powered models comprised two essential components: a grammatical error correction model and a grammaticality classifier. When users harness the grammar check feature, their queries are subjected to correction by the model before undergoing validation by the classifier. This two-step process guarantees that users are presented with only accurate corrections, mitigating the risk of erroneous or perplexing suggestions.
Conclusion:
Google’s introduction of EdiT5 and its grammar correction feature signifies a significant leap in the market. This innovation enhances search engine capabilities, offering users efficient and accurate grammar correction, ultimately improving user experience and setting a new industry standard. It underscores Google’s commitment to providing reliable and precise search results.