TL;DR:
- Max Planck Institute researchers introduced PoseGPT, a framework powered by large language models (LLMs) for understanding 3D human poses.
- Good posture is essential for health and well-being, influencing muscle, joint, and ligament alignment, lung expansion, and overall mood.
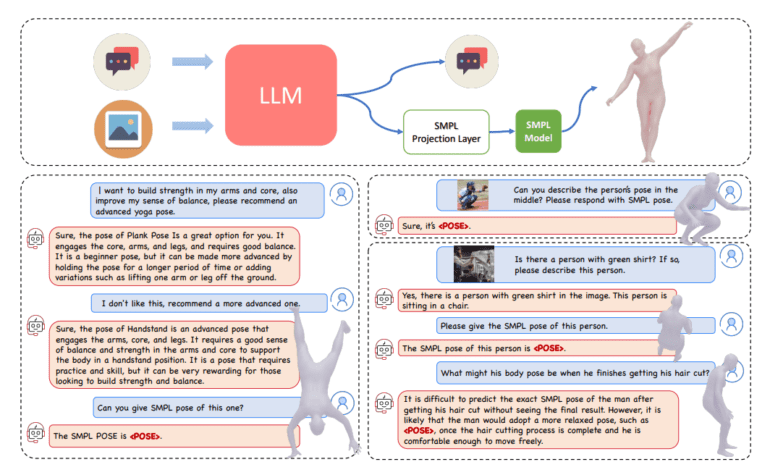
- PoseGPT enables the direct generation of 3D body poses from textual descriptions or images by embedding SMPL poses as tokens.
- The model uses an MLP to predict SMPL pose parameters, offering flexibility in input and output modalities.
- While accuracy in classical tasks may need improvement, PoseGPT’s potential lies in its ability to leverage inherent world knowledge for nuanced reasoning about human poses.
- Unlike traditional pose regression, PoseGPT doesn’t rely on cropped bounding boxes, allowing it to understand poses in context.
- The model can generate human poses and comprehend complex verbal and visual inputs, opening doors to novel applications.
Main AI News:
In the realm of health, well-being, and daily life, human posture holds a pivotal role. It dictates the alignment and arrangement of the body while sitting, standing, or reclining. The significance of maintaining good posture cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in optimizing the coordination of muscles, joints, and ligaments, thus mitigating the risk of muscular imbalances, joint discomfort, and overuse injuries. Furthermore, it facilitates the even distribution of the body’s weight, averting undue strain on specific body regions.
Moreover, proper posture fosters enhanced lung expansion and supports efficient breathing. In contrast, slouching or poor posture can constrict the chest cavity, limiting lung capacity and impeding the process of respiration. Additionally, maintaining good posture contributes to healthy blood circulation throughout the body. Research has indicated that upholding an upright and open posture exerts a positive influence on one’s mood and self-confidence. The adoption of such a posture is associated with heightened assertiveness, a more positive outlook, and reduced stress levels.
Enter PoseGPT, a groundbreaking framework developed by a collaborative team of researchers hailing from the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, ETH Zurich, Meshcapade, and Tsinghua University. This innovative framework harnesses the power of Large Language Models (LLMs) to decipher and rationalize 3D human poses, whether derived from images or textual descriptions. Traditional methods for human pose estimation, be it image-based or text-based, often fall short in their ability to grasp holistic scene comprehension and nuanced reasoning, leading to a disconnection between visual data and its real-world implications.
PoseGPT boldly addresses these limitations by introducing SMPL poses as distinct signal tokens within a multimodal LLM, thereby enabling the seamless generation of 3D body poses from both textual and visual inputs.
The methodology employed embeds SMPL poses as a unique token, prompting the LLM to produce them when queried about SMPL pose-related inquiries. Subsequently, the language embedding is extracted from this token, and a Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) is employed to predict the SMPL pose parameters directly. This groundbreaking approach empowers the model to accept input in the form of either text or images and deliver 3D body poses as output.
The research team subjected PoseGPT to a battery of diverse tasks, ranging from traditional 3D human pose estimation based on a single image to the generation of poses from textual descriptions. While the metric accuracy on these classical tasks may require further refinement, it stands as an initial proof of concept. More significantly, once LLMs comprehend SMPL poses, they can leverage their inherent knowledge of the world to establish correlations and draw reasoned conclusions about human poses, without the need for extensive additional data or training.
In a departure from conventional approaches to pose regression, the methodology employed by PoseGPT does not involve limiting the multimodal LLM to a cropped bounding box centered around the individual in question. Instead, the model is exposed to the entire scene, affording it the ability to formulate inquiries pertaining to individuals and their respective poses within the broader context.
As the LLM grasps the intricacies of 3D body pose, it acquires a dual capability: not only can it generate human poses, but it can also comprehend the world at large. This newfound capability empowers it to navigate complex verbal and visual inputs, ultimately resulting in the development of human poses. This, in turn, paves the way for novel tasks that were previously beyond the reach of existing models, complete with benchmarks to gauge performance effectively.
Conclusion:
The introduction of PoseGPT marks a significant leap in the field of understanding 3D human poses. Its innovative approach, leveraging Large Language Models, has the potential to revolutionize various industries, from healthcare and fitness to augmented reality and gaming. The ability to generate and reason about human poses from diverse inputs will likely lead to the development of innovative products and applications, shaping the market’s future. Businesses should keep a close eye on PoseGPT’s advancements and consider its integration into their solutions for enhanced user experiences and data-driven insights.