TL;DR:
- MVHumanNet, a vast dataset, is introduced with 4,500 human identities and extensive annotations.
- It supports research in various 2D/3D human-centric tasks, including action recognition and image generation.
- MVHumanNet addresses limitations in existing datasets, offering diverse data and innovative potential.
- The dataset’s scale enables advanced research and innovations in multi-view human sequences.
- Pilot studies demonstrate its effectiveness in enhancing performance across various visual tasks.
- MVHumanNet is a valuable resource for researchers and developers working on human-centric applications.
Main AI News:
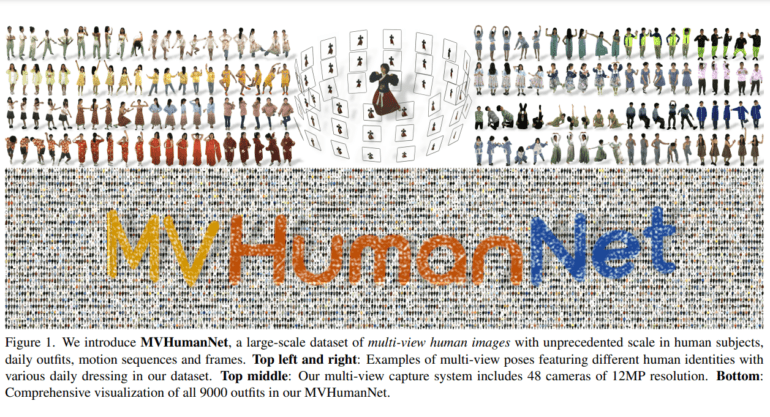
In a groundbreaking development, researchers from FNii CUHKSZ and SSE CUHKSZ have unveiled MVHumanNet, an expansive dataset poised to redefine the landscape of multi-view human action sequences. With a staggering 4,500 human identities, MVHumanNet emerges as a game-changer, equipped with an array of meticulously curated annotations, encompassing human masks, camera parameters, 2D and 3D key points, SMPL/SMPLX parameters, and textual descriptions.
MVHumanNet’s significance lies in its capacity to galvanize advancements in a multitude of domains, including action recognition, human NeRF reconstruction, text-driven view-unconstrained human image generation, and 2D/3D avatar creation. This transformative dataset seeks to fuel innovation on a grand scale in the realm of 3D human-centric tasks.
Breaking free from the constraints of existing datasets, MVHumanNet’s comprehensive offerings, which encompass human masks, camera parameters, 2D/3D key points, SMPL/SMPLX parameters, and textual descriptions, serve as a beacon for researchers embarking on ambitious 2D/3D human-centric projects. These encompass action recognition, NeRF reconstruction, text-driven image generation, and 2D/3D avatar creation. MVHumanNet’s release marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of large-scale 3D human-centric endeavors.
Acknowledging the paramount role played by large-scale datasets in the realm of AI, particularly in language and text-to-image models, the research underscores a stark disparity in progress within human-centric tasks due to the dearth of extensive human datasets. The prevailing 3D human datasets yearn for more diversity in terms of identities and clothing. In response, MVHumanNet makes its grand entrance, geared towards catalyzing innovations in the expansive arena of 2D/3D visual tasks linked to human-centric activities on a monumental scale.
Harnessing the capabilities of a scalable multi-view human system, this dataset acts as a catalyst for diverse 2D and 3D visual tasks, including action recognition, NeRF-based human reconstruction, text-driven image generation, and avatar creation. Researchers have harnessed generative models such as StyleGAN2 and GET3D to synthesize 2D and 3D human images, capitalizing on the dataset’s sheer scale. MVHumanNet serves as a crucible for research and innovations in a multitude of human-centric domains on an unprecedented scale.
MVHumanNet is an extensive repository capturing multi-view human sequences, boasting a staggering 4,500 identities, 9,000 outfits, and a wealth of annotations. Initial pilot studies employing MVHumanNet have already demonstrated remarkable performance enhancements and efficiency in a diverse array of 2D and 3D visual tasks, spanning from action recognition to NeRF-based reconstruction, text-driven image generation, and avatar creation. The dataset’s massive collection of real-captured multi-view data amplifies the potential for text-driven realistic human image generation, nurturing an ecosystem of diverse and comprehensive human image synthesis.
MVHumanNet stands as an invaluable asset for researchers and developers engaged in an array of visual tasks connected to human-centric applications. With its exhaustive multi-view captures, extensive annotations, and vast real-captured dataset, it is primed to spearhead further innovations, revolutionizing domains such as action recognition, human NeRF reconstruction, text-driven image generation, and avatar creation. MVHumanNet’s contribution to diverse image synthesis, complete with pose variations, underscores its indispensability as a tool for large-scale 3D human-centric endeavors.
Looking forward, the research community recommends the public release of the MVHumanNet dataset, complete with annotations, laying the foundation for future exploration in the burgeoning 3D digital human sphere. Researchers intend to explore opportunities to expand training datasets comprehensively, with stringent regulations in place to mitigate potential negative social impacts stemming from its usage.
Conclusion:
MVHumanNet’s arrival signals a significant step forward in the field of 3D human-centric tasks. With its comprehensive dataset and diverse applications, it promises to drive innovation and performance gains in action recognition, image generation, and more. This development is poised to create new opportunities and solutions within the market for AI-driven human-centric applications.