TL;DR:
- InseRF, developed by ETH Zurich and Google Zurich, redefines 3D scene generation.
- It enables seamless insertion of objects into 3D scenes through a text-guided 2D approach.
- InseRF’s methodology involves a meticulous five-step process for object insertion.
- Monocular depth estimation and optimization ensure accurate object placement.
- The fusion of scene and object NeRFs enhances scene quality with lighting and texture improvements.
Main AI News:
In the realm of 3D scene generation, the challenge of seamlessly integrating new elements into existing environments has long perplexed researchers and developers. The quest for enhancing these digital landscapes with a touch of human-like creativity and intent has been hindered by the difficulty of inserting objects consistently across various viewpoints, particularly when precise spatial guidance is unavailable.
Enter InseRF, a groundbreaking collaboration between ETH Zurich and Google Zurich that promises to reshape the way we manipulate 3D scenes. InseRF leverages a unique blend of textual descriptions and a single-view 2D bounding box to streamline the process of inserting objects into neural radiance field (NeRF) reconstructions of 3D environments. This approach marks a departure from traditional methods that often struggle with multi-view consistency or demand intricate spatial data.
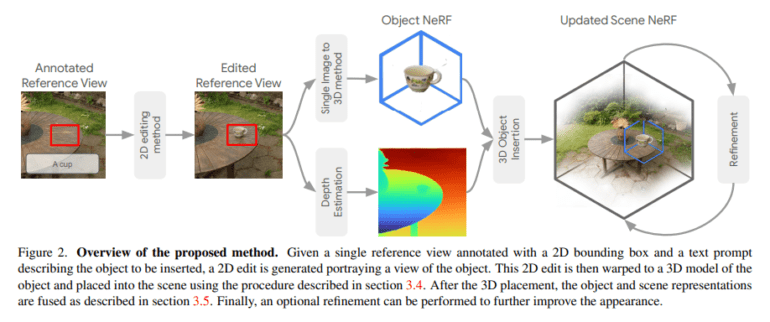
At the heart of InseRF lies a meticulously designed five-step methodology. The journey commences by creating a 2D representation of the target object in a chosen reference view of the scene. This critical step relies on a text prompt and a 2D bounding box to guide the spatial arrangement and appearance of the object. Utilizing advanced single-view object reconstruction techniques, the object transcends its 2D form and takes its place in the 3D realm. These techniques draw from extensive 3D shape datasets, instilling strong priors regarding the geometry and aesthetics of 3D objects.
InseRF taps into the potential of monocular depth estimation methods to gauge the object’s depth and position concerning the camera in the reference view. An intricate dance of scale and distance optimization follows, ensuring the object’s placement in 3D space faithfully mirrors its intended size and location, as dictated by the reference view.
The fusion of scene and object NeRFs forms the bedrock of InseRF’s approach, resulting in a harmonious scene enriched by the newly inserted object. This fusion is achieved by converting rays into the scene and object coordinate systems and applying each NeRF representation to the corresponding transformed rays. An optional yet indispensable refinement step takes this process further, elevating the scene’s quality with enhancements in lighting and texture for the inserted object.
InseRF promises to revolutionize the way we manipulate 3D scenes, offering a fresh perspective on object insertion that opens up exciting possibilities for creative and practical applications. With its innovative blend of textual guidance and spatial understanding, InseRF is poised to redefine the boundaries of 3D scene generation.

Source: Marktechpost Media Inc.
Conclusion:
InseRF represents a significant breakthrough in the field of 3D scene manipulation. Its ability to seamlessly insert objects through a unique text-guided 2D approach offers new possibilities for industries like gaming, virtual reality, and architecture. This innovation is set to drive market growth, catering to the demand for more dynamic and realistic 3D environments in various applications.