TL;DR:
- Language Agents with Large Language Models (LLMs) are revolutionizing computational linguistics.
- Uncertainty management is a critical challenge in language processing, especially in generative tasks.
- Traditional methods employ multiple outputs and voting, but UALA introduces a novel approach.
- Uncertainty-Aware Language Agents (UALAs) evaluate response uncertainty, improving question-answering.
- This innovation integrates uncertainty estimation without additional training, delivering superior results.
- UALA significantly outperforms standard fine-tuning, reduces tool usage, and excels with less training data.
Main AI News:
Language Agents have ushered in a transformative era in computational linguistics, propelling OpenAI and LLaMA to the forefront of innovation. These agents harness the power of Large Language Models (LLMs) to engage with and process information from the external world. With ingenuity in utilizing tools and APIs, these agents autonomously acquire and seamlessly assimilate new knowledge, marking a significant leap forward in the realm of complex reasoning tasks.
A pivotal challenge that confronts Language Agents is the intricate art of managing uncertainty within the realm of language processing. This challenge becomes particularly pronounced in tasks that involve generative models, such as machine translation and summarization, where precision and reliability are non-negotiable prerequisites.
In addressing the enigma of uncertainty, traditional approaches in natural language generation (NLG) often resort to employing multiple candidate outputs and resorting to majority voting methods. Techniques like Self-Consistency and Minimum Bayes-Risk Decoding have earned their stripes in domains demanding meticulous precision and fact-based responses.
Breaking away from convention, the research introduces an avant-garde method that seamlessly incorporates uncertainty estimation into the decision-making process of language agents. Crafted by a formidable team of researchers, this method takes a novel approach, centering on the augmentation of the agents’ capacity to process and respond to linguistic inputs with unparalleled precision.
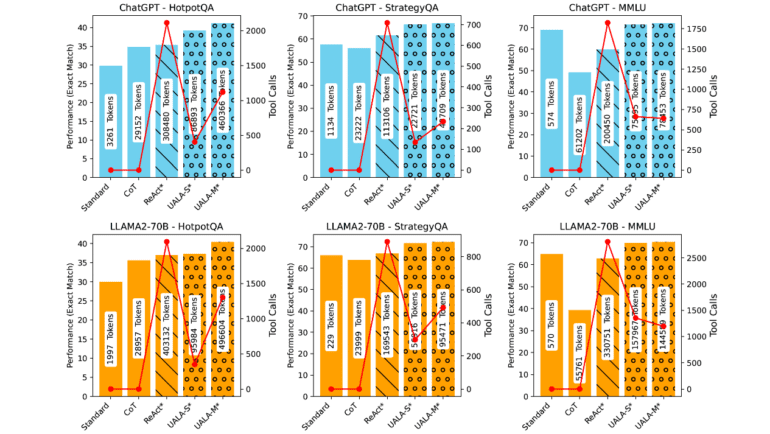
The bedrock of this pioneering research rests upon the concept of Uncertainty-Aware Language Agents (UALAs). These astute agents embark on a journey to evaluate the uncertainty shrouding the responses they generate. Armed with this valuable insight, they make discerning choices – whether to embrace these responses or embark on a quest for external resources, thus optimizing their performance in a multitude of question-answering scenarios.
The methodology underpinning this research is nothing short of revolutionary and intricate in equal measure. Researchers have painstakingly constructed a framework that seamlessly integrates uncertainty estimation into the thought process and decision-making faculties of language agents. This process entails the meticulous measurement of uncertainty in generated responses, followed by a decisive call to either accept or seek additional information through external resources. Remarkably, this approach does not necessitate additional training for the agent, drawing inspiration from the principles of few-shot learning and consistently enhancing the agent’s performance across a diverse spectrum of question-answering tasks, irrespective of the underlying LLM’s size.
The results underscore the resounding success of this methodology. The Uncertainty-Aware Language Agent (UALA) method has demonstrated unparalleled prowess, outclassing conventional and existing fine-tuning techniques in question-answering domains. Most notably, it has managed to curtail the frequency of tool usage by nearly half, all while upholding the hallmark of high-quality outcomes. Its efficacy has remained unwavering across diverse tool-use frameworks, showcasing its adaptability and the extent of its generalization capabilities. Furthermore, the research has uncovered a startling revelation: UALA exhibits superior performance improvements even with limited training data, outshining traditional fine-tuning methods, and underscoring its efficiency.
Conclusion:
The introduction of Uncertainty-Aware Language Agents (UALAs) marks a significant advancement in language processing, offering enhanced precision, adaptability, and efficiency. This development is poised to reshape the market by providing more reliable and effective solutions for complex language-related tasks, potentially attracting a broader range of industries and applications.