- Recent analysis co-authored by Google researchers reveals the rapid growth of AI-generated misinformation.
- The research introduces a comprehensive dataset dating back to 1995, highlighting the prevalence of AI manipulation.
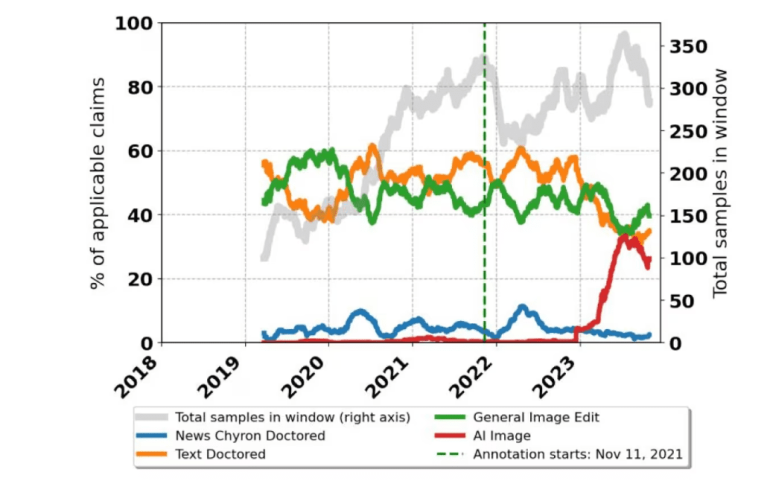
- AI-generated content, particularly images, has become as common as traditional forms of manipulation, fueled by advancements in AI image-generation tools.
- Despite a slowdown in fact-checking AI, video hoaxes constitute a significant portion of fact-checked claims involving media.
- Efforts to combat AI-generated misinformation include initiatives like digital watermarking, with calls for collaborative standardization efforts among tech companies.
Main AI News:
The rapid proliferation of misinformation facilitated by artificial intelligence (AI) technology is a pressing concern in the digital landscape. Recent analysis, co-authored by Google researchers, sheds light on the alarming pace at which this phenomenon is escalating.
Published in a preprint last week and co-authored by researchers from Google, Duke University, and various fact-checking and media entities, the research introduces an extensive dataset of misinformation dating back to 1995, sourced from platforms like Snopes.
According to the findings, AI-generated content, particularly images, has surged in prevalence, now rivaling more conventional forms of manipulation. This trend is underscored by the emergence of new AI image-generation tools from major tech players like OpenAI, Microsoft, and Google.
The study points out a correlation between the rise of fact-checking AI and the heightened attention surrounding AI technologies, indicating a potential focus shift among online platforms. However, recent months have seen a slowdown in fact-checking AI, with textual and image manipulations experiencing a resurgence.
Further analysis reveals that video hoaxes constitute a significant portion, approximately 60%, of fact-checked claims involving media, highlighting the multifaceted nature of contemporary misinformation.
Despite efforts to combat AI-generated misinformation, challenges persist. Sasha Luccioni, a prominent AI ethics researcher at Hugging Face, emphasizes the sheer volume of AI-generated content, making it difficult to monitor effectively.
Instances of AI-generated content, ranging from fake nude images of celebrities to deceptive photographs, continue to permeate online spaces, prompting tech companies like Google to implement countermeasures. These include initiatives such as digital watermarking, aimed at identifying AI-generated images, and exploring visible watermark options for creators.
Collaborative efforts among tech giants to establish AI watermarking standards could offer a viable solution to mitigate the proliferation of AI-driven misinformation, suggests Luccioni.
As the battle against AI-driven misinformation intensifies, it’s imperative for stakeholders to prioritize proactive measures and foster collaboration to safeguard the integrity of digital content ecosystems.
Conclusion:
The escalating prevalence of AI-driven misinformation, as evidenced by recent research findings, poses significant challenges for the market. It underscores the urgent need for collaborative efforts among stakeholders to develop and implement effective countermeasures, such as standardized AI watermarking, to preserve the integrity of digital content ecosystems and uphold consumer trust in online platforms. Failure to address this issue comprehensively could result in heightened skepticism among users and potential reputational damage for tech companies implicated in the dissemination of AI-generated misinformation.