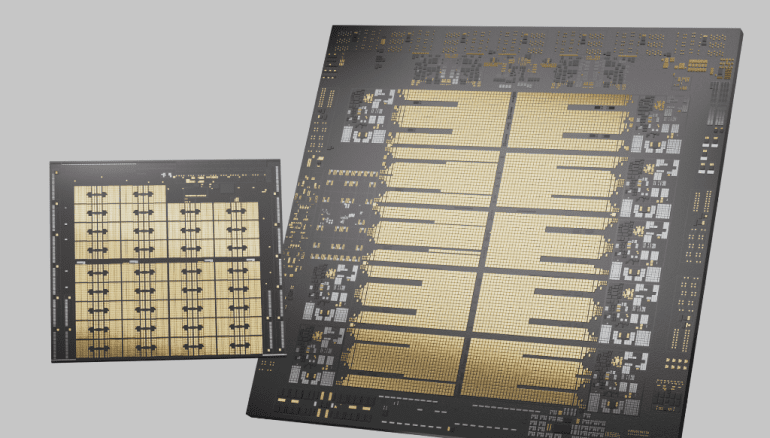
- IBM introduced the Telum II Processor at Hot Chips 2024, designed for next-gen mainframe systems.
- The Telum II features eight high-performance cores with a 40% increase in on-chip cache capacity.
- Enhanced AI accelerator integrated for low-latency, high-throughput AI inference operations.
- New Data Processing Unit (DPU) improves overall efficiency, boosting I/O density by 50%.
- IBM also unveiled the Spyre Accelerator, which is optimized for complex AI models, including generative AI.
- Telum II and Spyre provide a scalable architecture for ensemble AI methods, improving AI accuracy.
- IBM aims to lead the way in delivering secure, power-efficient enterprise computing solutions.
Main AI News:
At the Hot Chips 2024 conference held at Stanford University, IBM Corp. introduced the specifications of its highly anticipated Telum II Processor. This advanced chip is set to power the next generation of IBM’s iconic mainframe systems, driving them to the forefront of artificial intelligence processing.
The Telum II Processor, a successor to the original Telum chip launched in 2021, is equipped with eight high-performance cores at 5.5 gigahertz, each with 36 megabytes of memory. This configuration leads to a 40% increase in on-chip cache capacity, totaling 360 megabytes. The processor also features an enhanced AI accelerator explicitly designed for low-latency, high-throughput AI inference operations. It is particularly well-suited for applications like real-time fraud detection in financial transactions.
A key innovation in Telum II is the introduction of a new Data Processing Unit (DPU), which offloads specific computing tasks to improve the chip’s overall efficiency. The DPU accelerates complex input/output protocols for networking and storage, resulting in a 50% increase in overall I/O density.
In tandem with the Telum II, IBM also unveiled the IBM Spyre Accelerator, a high-performance, enterprise-grade AI accelerator. Designed to complement the Telum II, the Spyre Accelerator is engineered to enhance the performance of complex AI models, including generative AI applications. It features 1 terabyte of memory spread across eight cards within a regular I/O drawer and 32 compute cores supporting multiple data types, such as int4, int8, fp8, and fp16. This architecture optimizes latency and improves throughput across various AI applications.
The Telum II and Spyre Accelerator combination provides a scalable architecture that supports ensemble AI methods. These methods leverage multiple machine learning and deep learning models alongside encoder large language models (LLMs) to achieve more accurate and robust AI outcomes.
By integrating the Telum II processor and Spyre accelerator into its systems, IBM is a leader in delivering high-performance, secure, and power-efficient enterprise computing solutions that address AI’s increasing demands. As IBM prepares to launch its next-generation mainframes later this year, it is poised to make significant advancements in computing performance, memory capacity, and AI capabilities, reinforcing its leadership in the enterprise computing space.
Conclusion:
IBM’s introduction of the Telum II Processor and Spyre Accelerator marks a significant step forward in the evolution of enterprise computing, particularly in AI-driven applications. These innovations enhance IBM’s mainframe capabilities and position the company to meet the growing demands of AI processing in the market. The focus on improved performance, efficiency, and scalability suggests that IBM is set to strengthen its leadership in the enterprise computing space, potentially influencing competitors to accelerate their advancements in AI and mainframe technologies. This move reinforces IBM’s commitment to staying ahead in the high-performance computing market, catering to industries where secure, real-time AI processing is critical.