TL;DR:
- AI-powered research identifies a groundbreaking material to reduce lithium usage in batteries.
- Microsoft and PNNL collaborated on a project using AI and HPC to analyze 32 million potential materials.
- The newly discovered solid-state electrolyte slashes lithium requirements by up to 70%.
- The demand for lithium is expected to rise significantly due to the growth of lithium-ion batteries in sustainable energy.
- AI’s potential extends beyond batteries, accelerating complex data-driven tasks in various fields.
Main AI News:
In a groundbreaking development that promises to reshape the landscape of energy storage, artificial intelligence (AI) has uncovered a revolutionary material poised to significantly reduce the reliance on lithium in batteries. Such discoveries, which once took years to unveil, can now be achieved in a matter of days, thanks to the exponential increase in computing power.
This cutting-edge material was recently unearthed through a collaborative effort between tech giant Microsoft and the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL). Leveraging advanced AI and high-performance computing (HPC), a cloud-based computational approach harnessing the collective power of numerous computers, the research team embarked on an ambitious quest.
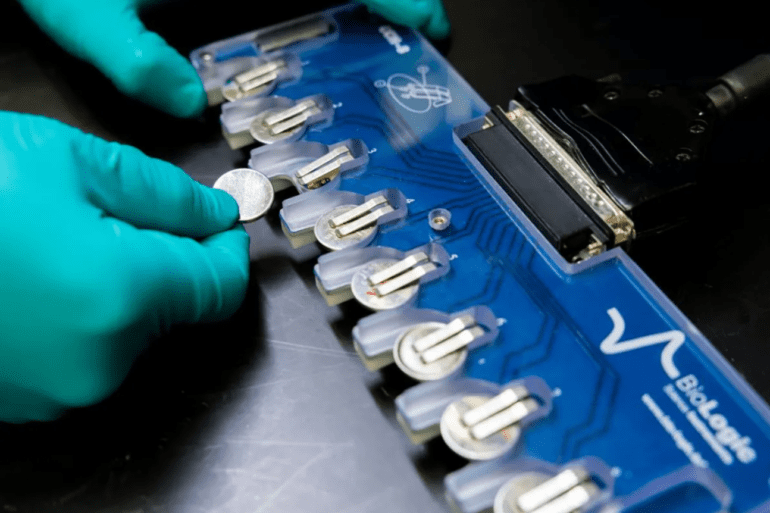
Their system meticulously scrutinized over 32 million potential inorganic materials, accomplishing a remarkable feat within a mere 80 hours: narrowing down the selection to 18 promising candidates with potential applications in battery development. Subsequent human testing revealed a particularly auspicious electrolyte among these candidates.
The significance of this discovery cannot be overstated, given the critical role lithium-ion batteries are poised to play in the global shift toward sustainable energy. The U.S. Department of Energy projects an astonishing five to tenfold surge in lithium demand by the decade’s end.
Nonetheless, numerous obstacles impede the seamless integration of lithium-ion batteries into our sustainable energy future. Natural lithium deposits remain relatively scarce, and the environmental and geopolitical ramifications of mining operations are substantial, fueling the need to seek alternative materials.
Enter the game-changing material: a solid-state electrolyte. It had long been assumed that the chemical properties of sodium and lithium ions would preclude their coexistence within a single solid-state electrolyte system. However, the AI-driven system defied convention, suggesting that such a material could indeed exist. Rigorous testing subsequently validated this groundbreaking proposition.
The unique electrolyte, utilizing both lithium and sodium, in addition to other elements, boasts a staggering 70% reduction in lithium requirements. This breakthrough prompted researchers from Microsoft and PNNL to synthesize the material and integrate it into functional prototype batteries, embarking on the rigorous journey of real-world testing.
AI’s potential for accelerating complex data-driven tasks extends well beyond battery research. Notably, AI has also played a pivotal role in the discovery of novel pharmacological compounds and drugs. In 2020, researchers at MIT harnessed specially designed computer algorithms to comb through an extensive digital archive comprising over 100 million chemical compounds, successfully identifying a potent antibiotic with the ability to combat superbugs.
As Brian Abrahamson, Chief Digital Officer at PNNL, aptly puts it, “We’re standing on the cusp of a new era in artificial intelligence, characterized by the maturation of AI models, the requisite computational power for training and practical use, and the capability to tailor them to specific scientific domains. This heralds an era of unprecedented acceleration, addressing challenges of global significance.”
Conclusion:
The AI-driven discovery of a revolutionary battery material that reduces lithium dependence by up to 70% marks a significant leap toward sustainable energy solutions. This breakthrough addresses the impending surge in lithium demand, offering a more environmentally friendly and geopolitically stable alternative. It exemplifies the transformative potential of AI in solving complex challenges, promising accelerated progress in various industries.