TL;DR:
- Amazon introduces AWS HealthScribe, a healthcare-focused generative AI service.
- The service transcribes and summarizes conversations between doctors and patients.
- Patient privacy is prioritized, and user data remains under their control.
- AI-driven medical documentation has been a growing trend since 2018.
- Microsoft subsidiary Nuance also announced a similar automated clinical documentation application.
- AWS HealthScribe integrates into existing clinical applications used by healthcare providers.
- Racial disparities in automated speech recognition require attention.
Main AI News:
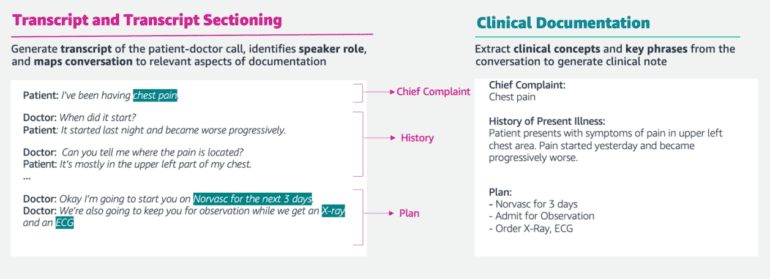
In a bid to revolutionize clinical documentation and reduce the time spent on administrative tasks, Amazon is rolling out a cutting-edge healthcare-focused generative AI service. Known as AWS HealthScribe, this HIPAA-eligible solution delves into the world of medical transcriptions by meticulously analyzing and transcribing conversations between healthcare professionals and patients.
Functioning as a digital stenographer, AWS HealthScribe creates a comprehensive written record of the dialogue between doctors and their patients, complete with a succinct summary of the essential points covered during the interaction. While this innovation streamlines the documentation process, it also emphasizes safeguarding patient privacy, as paramount in the healthcare domain.
Amazon is steadfast in its commitment to data security and patient confidentiality. The company has vowed not to employ inputs or outputs generated through the AWS HealthScribe service to train or improve its AI systems. Users retain complete authority over their data and have the autonomy to determine the most suitable storage options for their transcriptions and preliminary clinical notes.
The integration of large language models within the medical AI sector has been gaining traction since 2018. While researchers continue to explore the reliability of generative AI for producing clinical diagnoses, several transcription services akin to AWS HealthScribe’s offerings have emerged. In a similar vein, Microsoft subsidiary Nuance made waves with its announcement of a fully automated clinical documentation application in March.
It is important to note that AWS HealthScribe is designed as a service that seamlessly integrates into existing clinical applications utilized by healthcare providers, rather than a standalone application. Among the early adopters mentioned in Amazon’s announcement are prominent healthcare software vendors such as Babylon, 3M, and ScribeEMR.
As with any form of AI, automated speech recognition comes with its own set of challenges. Racial disparities, in particular, are a concern that necessitates careful monitoring and remediation to ensure fairness and inclusivity in healthcare AI applications.
Conclusion:
The introduction of Amazon’s AWS HealthScribe, an advanced HIPAA-eligible AI transcription service, signifies a significant step towards streamlining healthcare documentation processes. As the market embraces AI-driven solutions for medical documentation, it opens doors for further innovation and improved operational efficiency in the healthcare industry. However, addressing challenges such as racial disparities in automated speech recognition will be crucial to ensure fairness and inclusivity in healthcare AI applications. Businesses in the healthcare and AI sectors should keep a close eye on these developments and seize opportunities to integrate such transformative technologies into their offerings.