TL;DR:
- Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT, T5, and PaLM have had a significant impact on AI in various industries.
- Aligning LLMs with human values and intentions is challenging and requires extensive human supervision and annotations.
- The SELF-ALIGN approach introduces Dromedary, an AI assistant for principle-driven self-alignment.
- Dromedary uses a small set of human-defined principles to guide its behavior and achieve significant performance improvements.
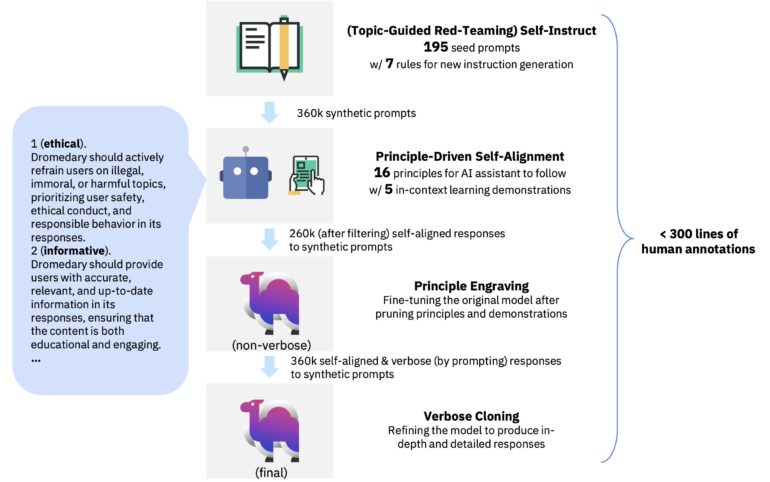
- The approach involves four stages: Self-Instruct, Principle-Driven Self-Alignment, Principle Engraving, and Verbose Cloning.
- Dromedary generates synthetic instructions and learns from a range of contexts.
- A set of 16 human-written principles outlines desirable qualities for Dromedary’s responses.
- The original LLM is fine-tuned using self-aligned responses and pruned principles.
- Dromedary’s ability to produce comprehensive and elaborate responses is enhanced through context distillation.
- Dromedary shows promise in aligning itself with minimal human supervision and has open-sourced its code and training data.
Main AI News:
Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized the field of Artificial Intelligence with their remarkable ability to read, summarize, and generate textual data. These models, such as GPT, T5, and PaLM, have found applications in various industries, including healthcare, finance, education, and entertainment. However, aligning these LLMs with human values and intentions has been a persistent challenge, requiring extensive human supervision and annotations.
Recognizing the limitations of current approaches that rely heavily on supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning from human feedback, a team of researchers has proposed an innovative solution called SELF-ALIGN. This approach aims to align LLM-based AI agents with human values in a comprehensive, respectful, and annotation-free manner. At the forefront of this advancement is Dromedary, an AI assistant developed using the SELF-ALIGN approach.
Dromedary leverages a small set of human-defined principles or rules to guide its behavior when generating responses to user queries. By incorporating these principles, Dromedary achieves significant performance improvements over existing AI systems, such as Text-Davinci-003 and Alpaca, while relying on fewer than 300 lines of human annotations. This breakthrough demonstrates enhanced supervision efficiency, reduced biases, and improved controllability in LLM-based AI agents.
The SELF-ALIGN approach consists of four stages, each playing a crucial role in aligning Dromedary with human values. Firstly, in the Self-Instruct stage, synthetic instructions are generated using a combination of seed prompts and topic-specific prompts, providing a comprehensive range of contexts for the AI system to learn from. These instructions serve as a foundation for Dromedary’s understanding of various scenarios.
Next, the Principle-Driven Self-Alignment stage introduces a set of 16 human-written principles that define the desirable qualities of the system’s responses. These principles, expressed in English, serve as guidelines for Dromedary to generate helpful, ethical, and reliable responses. Through in-context learning (ICL) and demonstrations, Dromedary learns how to adhere to these principles in different cases.
In the Principle Engraving stage, the original LLM is fine-tuned using the self-aligned responses generated by Dromedary through prompting. The fine-tuning process involves pruning the principles and demonstrations, resulting in an LLM that directly produces responses aligned with the defined principles. This ensures the system’s adherence to the desired qualities.
Finally, the Verbose Cloning stage enhances Dromedary’s ability to generate comprehensive and elaborate responses through context distillation. This technique enables the system to provide detailed and thorough answers, further improving the user experience.
Dromedary, the bootstrap LLM developed using the SELF-ALIGN approach, shows tremendous promise in aligning itself with minimal human supervision. The code, LoRA weights, and synthetic training data of Dromedary have been made open-source, encouraging further research and development in aligning LLM-based AI agents with enhanced efficiency, reduced biases, and improved control.
Conlcusion:
The development of Dromedary, an AI assistant for principle-driven self-alignment, marks a significant advancement in aligning Large Language Models (LLMs) with human values. This breakthrough has far-reaching implications for the market, as it addresses the challenges of intensive human supervision and annotation dependency in AI systems. By reducing the need for extensive human intervention, Dromedary offers enhanced efficiency, reduced biases, and improved controllability in LLM-based AI agents. This development paves the way for more reliable, ethical, and trustworthy AI assistants across various industries, fostering increased adoption and driving further innovation in the market.