- A team from the University of Cambridge introduces CheckMate, an open-source platform for evaluating AI-powered chatbots.
- Experimentation reveals the nuanced efficacy of LLMs like InstructGPT, ChatGPT, and GPT-4 in assisting users with undergraduate-level mathematics problems.
- Despite occasional inaccuracies, LLMs often provide beneficial support to users, especially in chat-oriented scenarios.
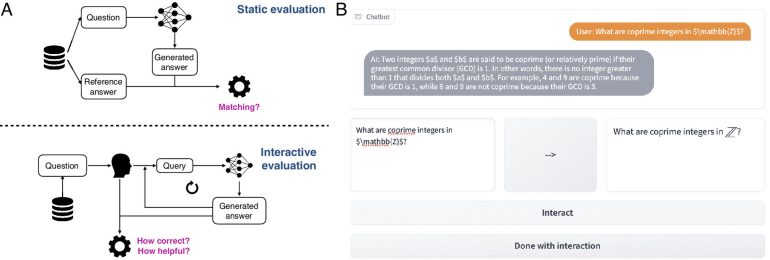
- CheckMate’s dynamic evaluation approach challenges traditional static methods, offering insights into the contextual appropriateness of LLM responses.
- Human evaluation alongside CheckMate uncovers the intricate interplay between user confidence and perception of LLM-generated outputs.
Main AI News:
In a groundbreaking endeavor led by the University of Cambridge, a consortium of computer scientists, engineers, mathematicians, and cognitive scientists has unveiled CheckMate, an open-source evaluation platform set to redefine the landscape of assessing large language models (LLMs).
The genesis of CheckMate emerged from a comprehensive experiment orchestrated by the research team. They put three prominent LLMs — InstructGPT, ChatGPT, and GPT-4 — to the test, enlisting human participants to tackle undergraduate-level mathematics quandaries with their assistance.
The study scrutinized the efficacy of LLMs in aiding participants, revealing a positive correlation between correctness and perceived helpfulness. However, intriguingly, instances arose where despite inaccuracies, LLMs proved beneficial to participants. Notably, certain erroneous outputs were erroneously perceived as correct, particularly in chat-optimized LLMs.
The findings, documented in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, underscore the imperative of not only quantitatively evaluating LLM performance but also assessing their synergy with human users. Albert Jiang, co-first author from Cambridge’s Department of Computer Science and Technology, emphasized the necessity of comprehensive evaluation frameworks in human-LLM interactions.
Traditionally, LLM evaluation hinges on static input-output pairs, neglecting the dynamic nature of chatbots and their contextual appropriateness. CheckMate, a pioneering solution tailored for applications in mathematics, addresses this lacuna, heralding a new era in LLM appraisal.
Katie Collins, co-first author from the Department of Engineering, elaborated on the dichotomous perceptions prevalent among mathematicians regarding LLM capabilities, highlighting the quest for delineating tasks suitable for LLMs.
Engaging 25 mathematicians across diverse expertise levels, the researchers navigated through the labyrinth of LLM performance evaluation using CheckMate. Participants interacted with LLMs sans knowledge of their identities, rating responses for correctness and helpfulness.
Noteworthy was the discovery of LLM fallibility juxtaposed with human error. Participants’ confidence in their problem-solving prowess significantly influenced their perception of LLM-generated responses, illuminating the nuanced nature of human evaluation.
Jiang emphasized the burgeoning challenge of discerning LLM outputs amid their growing linguistic prowess, advocating for vigilant scrutiny by end-users. Leveraging insights from CheckMate, the researchers affirmed the collaborative potential of newer LLM iterations in tackling undergraduate-level math problems, contingent upon users’ discernment.
While LLMs offer unparalleled flexibility vis-a-vis traditional search engines, CheckMate’s applicability extends beyond mathematics, portending its utility across diverse domains. As Collins asserts, these evaluation tools furnish invaluable insights into LLM capabilities, albeit not as standalone problem-solving mechanisms.
Conclusion:
The emergence of CheckMate signals a pivotal shift in the evaluation of AI chatbots, emphasizing the need for nuanced assessment frameworks that consider both quantitative performance metrics and qualitative user interactions. This development underscores the growing importance of user-centric AI solutions in diverse market segments, from education to customer service, where AI chatbots play a pivotal role in enhancing user experiences and productivity. Companies invested in AI development must prioritize user feedback and iterative improvement to ensure the seamless integration of AI technologies into everyday workflows.