- Harvard and Google researchers collaborated on a groundbreaking project to create a detailed 3D map of a tiny section of the human brain.
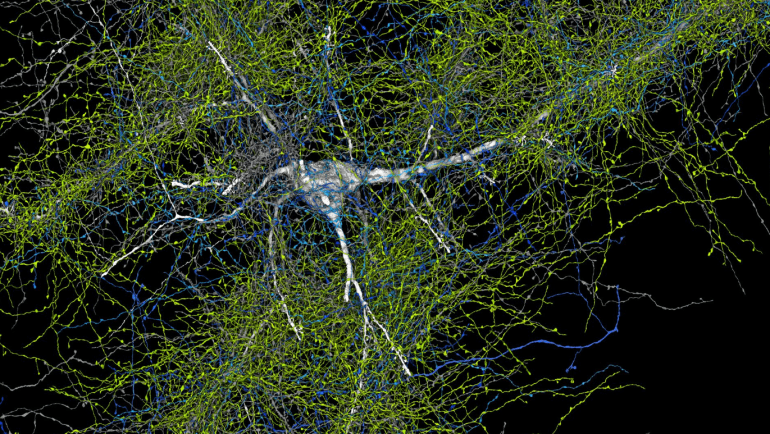
- The map reveals over 57,000 neurons, 9 inches of blood vessels, and 150 million synapses, providing unprecedented insights into brain structure.
- Utilizing advanced microscopy and AI, the team achieved nanometer-scale resolution, surpassing previous imaging techniques.
- The brain fragment, sourced from a 45-year-old epilepsy patient, underwent meticulous processing and imaging, generating 1.4 petabytes of data.
- Intriguing discoveries include axonal whorls and rare synapse-rich connections, shedding light on brain function and neurological conditions.
Main AI News:
In a groundbreaking collaboration between Harvard University and Google, researchers have crafted an extraordinary 3D map of a minute segment of the human brain, marking an unparalleled leap in scientific understanding. This monumental endeavor, spanning over a decade, meticulously delineates the intricacies of over 57,000 neurons, 9 inches of blood vessels, and a staggering 150 million synapses—the synaptic connections crucial for brain function.
Dr. Jeff Lichtman, co-leader of this pioneering project and professor of molecular and cellular biology at Harvard, expressed astonishment at the unprecedented level of detail attained. “I had never seen anything like this before,” he revealed in an interview with Live Science, underscoring the magnitude of this achievement.
The human brain, a marvel of complexity with roughly 170 billion cells, has long remained a tantalizing frontier for researchers. While previous imaging techniques offered glimpses into its structure at varying scales, the marriage of advanced microscopy and artificial intelligence has now catapulted our comprehension to unparalleled heights.
Employing state-of-the-art microscopy methods and harnessing the power of machine learning, Lichtman and his team have transcended previous limitations, capturing the brain’s intricate architecture at a nanometer scale—a feat hitherto deemed unattainable. This nanoscale 3D map, constructed from a mere cubic millimeter of brain tissue, surpasses all prior resolutions, providing an unprecedented glimpse into the brain’s inner workings.
The journey to this groundbreaking revelation began with a small tissue sample extracted from the cerebral cortex of a 45-year-old woman undergoing epilepsy treatment. Through meticulous processing and staining techniques, the researchers transformed this sample into over 5,000 ultra-thin slices, each a mere 30 nanometers thick—an astonishing feat comparable to a thousandth of a hair strand’s width.
These slices, meticulously scrutinized using high-speed electron microscopy, yielded an avalanche of data, totaling a staggering 1.4 petabytes. Leveraging Google’s expertise in AI and machine learning, researchers meticulously analyzed this trove of information, reconstructing the brain’s intricate network in stunning detail.
Viren Jain, co-leader of the project and a senior staff scientist at Google, emphasized the pivotal role of advanced algorithms in this endeavor. “The amount and complexity of the data generated in this project required Google’s ability to develop state of the art machine learning and AI algorithms,” Jain highlighted, elucidating the symbiotic relationship between technology and neuroscience.
Amidst the labyrinth of neural pathways, researchers unearthed tantalizing revelations. Intriguingly, they discovered axonal whorls—knotted formations within neurons, described by Jain as “mysterious but beautiful.” Furthermore, they stumbled upon rare synapse-rich connections, hinting at novel mechanisms underlying rapid responses and memory encoding.
As the scientific community grapples with the implications of these findings, Lichtman remains cautiously optimistic. While the relevance of these discoveries to epilepsy and other neurological conditions remains uncertain, ongoing investigations promise to unravel the brain’s enigmatic tapestry.
Looking ahead, the team sets its sights on an even grander endeavor: mapping the entire mouse brain, a venture 500 times the scale of their current feat. Embarking on this ambitious odyssey, they aspire to unlock the secrets of cognition and memory, paving the way for transformative breakthroughs in neuroscience.
“The journey has just begun,” Lichtman affirmed, encapsulating the spirit of relentless inquiry propelling humanity towards a deeper understanding of the brain’s boundless complexity.
Conclusion:
The unveiling of Google AI’s revolutionary 3D brain map marks a paradigm shift in neuroscience, offering unparalleled insights into brain structure and function. This groundbreaking achievement not only deepens our understanding of the human brain but also paves the way for transformative advancements in healthcare, neurology, and AI-driven diagnostics. As researchers delve deeper into the mysteries of the mind, the implications for the market are profound, with potential applications ranging from personalized medicine to enhanced cognitive technologies.