- HPE, historically known for diverse compute engines, faces challenges in the AI server market.
- Despite acquisitions enhancing its HPC capabilities, HPE is the underdog in general-purpose servers.
- The AI market presents opportunities but also tensions among vendors, affecting collaboration.
- Catching up to Dell in AI server sales proves challenging for HPE, despite impressive growth.
- Both HPE and Dell grapple with profitability amid increased AI server sales.
- Financial restructuring adds complexity, with declining earnings before taxes despite rising server sales.
- GPU allocation challenges from suppliers like AMD and Nvidia hinder profitability.
- HPE remains committed to innovation, investing in GreenLake for flexible infrastructure solutions.
Main AI News:
In the ever-evolving realm of enterprise computing, Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) has long distinguished itself by offering a diverse array of compute engines, setting itself apart from its primary competitor, Dell, which has historically dominated the server market. However, as the tides of innovation continue to shift, HPE now finds itself in the unfamiliar position of the underdog in general-purpose servers. Despite this, strategic acquisitions of companies like SGI and Cray have catapulted HPE to the forefront of traditional High-Performance Computing (HPC) simulation machines.
Yet, even as HPE emerges as a dominant player in the realm of HPC, it faces a complex landscape in the burgeoning field of artificial intelligence (AI) servers. While the acquisitions of SGI and Cray have bolstered its capabilities in traditional HPC, the rapidly expanding AI market presents both opportunities and challenges for HPE. In particular, HPE must navigate a delicate balance of collaborating with vendors selling AI engines, despite underlying tensions and hostilities among these companies.
The dynamics of the AI server market pose significant challenges for HPE as it seeks to carve out a profitable niche in this competitive landscape. While it may seem prudent to align closely with Dell, given its historical dominance and established relationships in the market, customers stand to benefit from the presence of a strong competitor like HPE. Not only does competition drive innovation and lower costs, but HPE’s expertise can also help customers navigate the complex decision matrix of XPU supply chains across various vendors.
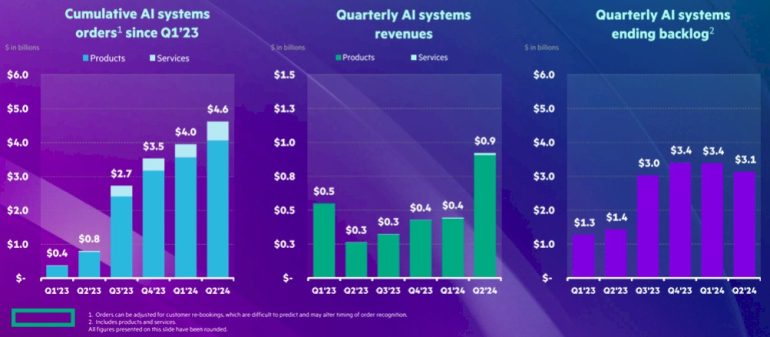
However, catching up to Dell in the AI server market is no easy feat for HPE. Despite its deep-rooted experience in supercomputing, HPE faces stiff competition from Dell, which reported a staggering $1.7 billion in AI system sales in its most recent quarter. In contrast, HPE’s AI server sales doubled to over $900 million, reflecting impressive growth but still trailing behind its rival.
Furthermore, both HPE and Dell grapple with the profitability of their AI server businesses. While the increase in AI server sales is undoubtedly a positive development, it’s essential to consider the impact on overall profitability. Dell, for instance, saw its margins decline, indicating that the additional AI server revenues failed to significantly boost its core systems business.
HPE’s financial restructuring adds another layer of complexity to its server sales landscape. While overall server sales witnessed a healthy increase, earnings before taxes for the Server group declined. This trend underscores the broader challenge facing HPE and its peers: balancing growth with profitability in a fiercely competitive market.
One of the primary hurdles for HPE in the AI server market is the allocation of crucial components, such as GPUs, from suppliers like AMD and Nvidia. AMD’s focus on supercomputers and Nvidia’s loyalty to Dell present formidable obstacles for HPE in securing sufficient GPU allocations. This scarcity, coupled with pricing pressures, exacerbates the profitability dilemma facing HPE and its peers.
Despite these challenges, HPE remains steadfast in its commitment to innovation and customer satisfaction. The company continues to invest in its GreenLake cloud-like pricing model, offering flexible infrastructure solutions to organizations worldwide. The growing popularity of GreenLake subscriptions underscores a broader shift towards software and services, reflecting changing customer preferences in the digital era.
Looking ahead, HPE anticipates a stronger second half, driven by AI systems, traditional servers, storage, networking, and GreenLake offerings. However, the transition from networking to AI systems presents margin challenges, highlighting the evolving landscape that HPE must navigate in pursuit of profitability. As the company charts its course in this dynamic market, it remains optimistic about its future prospects, driven by a relentless commitment to innovation and customer success.
Conclusion:
HPE’s struggles in the AI server market highlight the complexities of balancing growth with profitability in a competitive landscape. The challenges of securing crucial component allocations and declining margins underscore broader market dynamics. As HPE navigates these obstacles, its commitment to innovation and customer-centric solutions will be critical for future success.