TL;DR:
- NUS introduces NExT-GPT, an open-source multi-modal language model.
- NExT-GPT can process text, images, videos, and audio interchangeably.
- It offers a chat-based interface for diverse input and output formats.
- The model combines pre-trained encoders and decoders with innovative neural network layers.
- Most model parameters remain static during training, reducing costs while maintaining performance.
- NExT-GPT’s training dataset includes dialogues involving multiple modalities.
- It outperforms baseline models in multi-modal generation benchmarks.
- The model can generate modality-signaling tokens for specific content types.
- NExT-GPT empowers AI applications across various media types.
Main AI News:
NExT Research Center at the National University of Singapore (NUS) has introduced NExT-GPT, an open-source multi-modal large language model (LLM) named NExT-GPT. This cutting-edge innovation is tailored to effortlessly process text, images, videos, and audio, revolutionizing the landscape of AI applications across diverse media platforms.
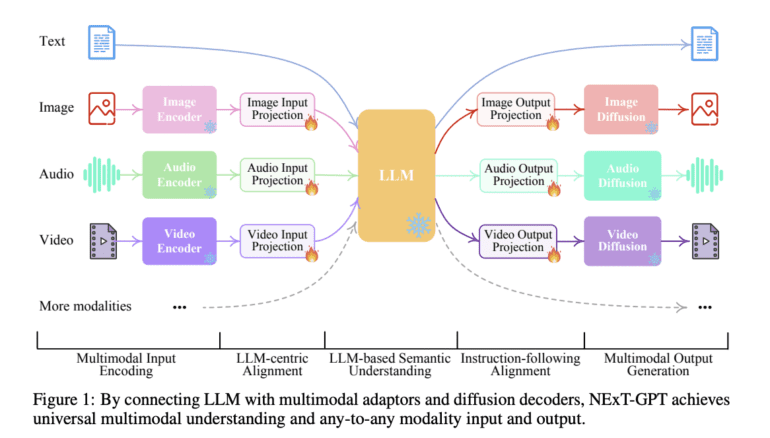
NExT-GPT sets the stage for a new era of AI capabilities, providing a versatile solution that can seamlessly accommodate a myriad of input types and deliver responses in various formats. Its dynamic chat-based interface empowers users to submit text, images, videos, or audio files, with the model adeptly comprehending and generating responses that align with the input’s nature. This multi-modal AI marvel merges pre-trained encoders and decoders, including the formidable Vicuna and Stable Diffusion, interspersed with adaptable neural network layers. These intermediary layers are honed through a cutting-edge technique devised by the NExT team, known as Modality-switching Instruction Tuning (MosIT).
The architecture of NExT-GPT stands on three pillars: an encoding stage featuring linear projections, the Vicuna LLM core responsible for token generation (including signals for output modalities), and a decoding stage furnished with modality-specific transformer layers and decoders. Significantly, a substantial proportion of the model’s parameters, encompassing encoders, decoders, and the Vicuna model itself, remain static during training, with merely around 1% undergoing updates. This judicious approach not only streamlines training expenses but also preserves top-notch performance standards.
The model’s training process hinges on instruction-tuning, leveraging a dataset comprising example dialogues between human users and chatbots. These dialogues encompass diverse scenarios involving multiple modalities in both input and output, amounting to approximately 5,000 dialogues.
When it comes to performance and evaluation, NExT-GPT consistently excels. It has been rigorously assessed across a spectrum of multi-modal generation benchmarks, consistently outperforming baseline models. Furthermore, human evaluators have consistently rated the model’s outputs across various scenarios, with image generation scenarios consistently garnering higher scores compared to video and audio.
One of NExT-GPT’s distinguishing features lies in its unique ability to generate modality-signaling tokens in response to user requests for specific content types, such as images, videos, or sounds. These tokens have been meticulously predefined and integrated into the LLM’s vocabulary during training.
The release of NExT-GPT marks a monumental stride forward, granting researchers and developers access to an exceptionally potent multi-modal language model. It is poised to catalyze the development of advanced AI applications spanning diverse media types, offering limitless possibilities for content generation, multimedia analysis, and virtual assistants capable of seamlessly interpreting and responding to user preferences in their preferred formats. NExT-GPT’s open-source availability signals a transformative moment in the realm of multi-modal AI, fostering innovation and integration across text, images, videos, and audio and heralding a new era of AI-driven possibilities.
Conclusion:
The introduction of NExT-GPT by NUS marks a significant advancement in multi-modal AI. This versatile model, with its ability to seamlessly handle diverse media types, has the potential to disrupt various markets, from content generation and multimedia analysis to virtual assistants. Its open-source nature fosters innovation and integration, making it a game-changer in the field of AI-driven applications.