TL;DR:
- Orca Security collaborates with Amazon Web Services (AWS) to enhance generative AI capabilities.
- Access to Amazon Bedrock service expands access to foundational LLMs and allows for custom LLM development.
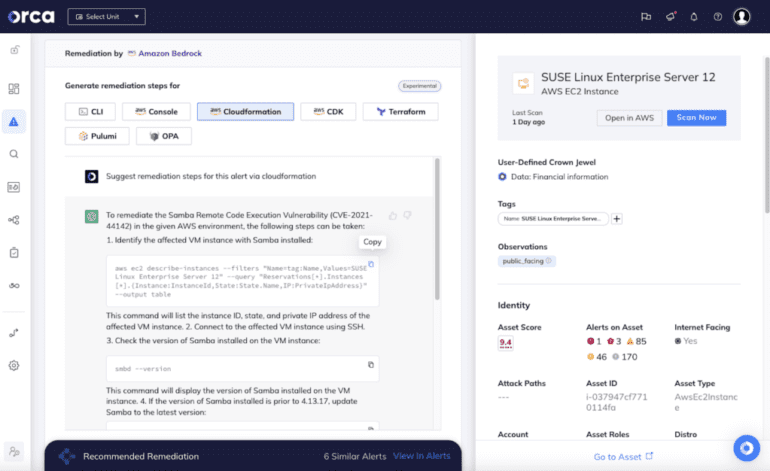
- Orca Cloud Security Platform can now automatically generate remediation instructions for cloud risks.
- CEO Gil Geron emphasizes the potential for faster response to cyber threats with generative AI.
- The combination of LLMs and data can revolutionize cybersecurity processes.
Main AI News:
In a strategic move, Orca Security has announced its collaboration with Amazon Web Services (AWS) to enhance its generative artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities. Building upon the large language models (LLMs) it already utilizes from Microsoft and OpenAI, Orca Security is expanding its horizons with access to the Amazon Bedrock service, which offers a robust collection of foundational LLMs. These models can be extended through vector databases, allowing organizations to harness external data for more comprehensive summarizations and recommendations.
One intriguing aspect of this collaboration is the possibility to craft custom LLMs, trained with specific datasets. This level of customization provides an unprecedented advantage to cybersecurity teams. With these enhanced capabilities, Orca Security’s Cloud Security Platform can now automatically generate remediation instructions for identified risks in cloud environments. Security teams and developers can seamlessly integrate the generated code into their command line interfaces or infrastructure-as-code (IaC) provisioning tools to promptly address vulnerabilities.
Gil Geron, the CEO of Orca Security, emphasized the evolving landscape of generative AI. He noted that as this technology continues to progress, cybersecurity teams will find it increasingly easier to respond to attacks. They will gain a deeper understanding of the attack nature, thanks to LLMs, and will be able to generate the necessary code for mitigation promptly. This improved responsiveness will enable cybersecurity teams to effectively counteract both potential threats and ongoing attacks.
Moreover, Orca Security plans to strategically deploy a mix of LLMs to tackle specific tasks and functions, providing a versatile approach to cybersecurity challenges.
While the full implications of generative AI on cybersecurity remain uncertain, it is conceivable that it could alleviate some of the stress associated with threat response. This, in turn, may reduce burnout among cybersecurity professionals and help bridge the gap between the demand for cybersecurity expertise and the limited pool of available talent.
Though cybersecurity teams will still need to collaborate with application developers to implement fixes, the process is expected to become more streamlined. A shared understanding of the threat nature across the DevSecOps workflow should facilitate smoother cooperation.
However, it’s important to note that cybercriminals will also have access to similar generative AI capabilities, ushering in an AI arms race. Organizations are now faced with the challenge of combating adversaries who possess the resources to experiment with emerging technologies. The proliferation of AI in this domain is undeniable, and there is no turning back.
In the grand scheme of things, cybersecurity teams stand to gain significantly from AI’s assistance in leveling the currently skewed playing field. Cybercriminal groups have grown increasingly sophisticated, making low-level attacks more common. If AI can automate responses to these lower-tier threats, cybersecurity teams can dedicate more time to investigating more nuanced and advanced threats.
Each cybersecurity team will need to make informed decisions about how to integrate LLMs with their data to advance cybersecurity. However, it is apparent that cybersecurity vendors are eager to support this transition. The primary concern now is ensuring that the data exposed to LLMs is handled securely and does not become accessible to unauthorized users seeking answers from these AI models.
Conclusion:
Orca Security’s partnership with Amazon represents a significant step in the evolution of generative AI for cybersecurity. This collaboration opens doors to more advanced threat response capabilities, potentially reducing stress on cybersecurity teams and addressing talent shortages in the industry. However, the growing use of generative AI by cybercriminals introduces new challenges, turning cybersecurity into an AI-driven arms race. Organizations must carefully manage data exposure to maintain security in this changing landscape.