- Phidata introduces a pioneering framework for autonomous AI assistants.
- Addresses limitations of traditional large language models (LLMs) by integrating long-term memory, contextual understanding, and actionable capabilities.
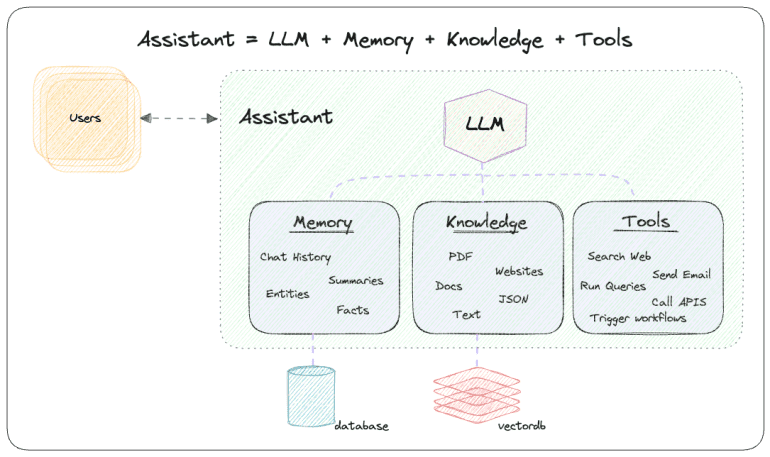
- Utilizes robust database infrastructure to store chat histories for sustained memory and contextually relevant responses.
- Empowers assistants to execute tasks autonomously by interfacing with external systems via streamlined function calls.
- Demonstrates versatility in applications, from generating investment reports to summarizing content from various sources.
Main AI News:
In today’s business landscape, the integration of artificial intelligence has become indispensable, particularly through the utilization of large language models (LLMs). Yet, these sophisticated systems encounter notable constraints. Chief among them is the challenge of retaining long-term conversational memory, thereby hindering the delivery of consistent and contextually informed responses. Moreover, the inherent incapacity of LLMs to execute actions autonomously, such as sending emails or accessing databases, further restricts their efficacy.
Presently, existing solutions offer only partial remedies to these issues. While some AI applications transiently store conversation logs, the data often dissipates post-session, resulting in repetitive and disjointed interactions. Similarly, tools facilitating API or database interactions necessitate manual intervention or extensive programming expertise for configuration and maintenance, failing to deliver a seamless autonomous experience.
Enter Phidata, a groundbreaking framework engineered to empower autonomous assistants, transcending the limitations inherent in conventional LLMs by seamlessly integrating long-term memory retention, contextual comprehension, and actionable capabilities. These assistants not only sustain prolonged dialogues but also execute tasks independently by interfacing with external systems.
Phidata operates by archiving chat histories within a robust database infrastructure, enabling assistants to uphold long-term memory and furnish contextually apt responses. Leveraging a vector database enhances the assistants’ comprehension of domain-specific contexts. Furthermore, Phidata facilitates task execution, such as data retrieval from APIs, email dispatch, or database querying, through streamlined function calls. This amalgamation of memory, comprehension, and functional versatility renders Phidata-powered assistants exceptionally adept.
Illustrating Phidata’s prowess are numerous exemplary use cases. It can orchestrate an AI-driven research aide proficient in crafting comprehensive investment reports through data analysis from diverse sources. Additionally, leveraging its advanced linguistic processing capabilities, Phidata can author news articles or distill content from YouTube videos, exemplifying its potential to revolutionize AI utilization within businesses, streamlining complex processes, and enhancing productivity.
Conclusion:
Phidata’s innovative framework marks a significant leap forward in the realm of AI assistants, addressing critical limitations of existing models. By seamlessly integrating long-term memory, contextual understanding, and autonomous action capabilities, Phidata not only enhances efficiency but also opens up new avenues for automation and productivity within businesses. Its potential to streamline complex tasks and deliver contextually relevant responses underscores its transformative impact on the market, paving the way for enhanced AI utilization and improved operational outcomes.