- Chinese scientists developed a brain-inspired AI model focused on internal complexity.
- The model addresses the limitations of traditional AI, such as high resource consumption.
- Research published in Nature Computational Science highlights advances toward more general-purpose AI.
- Current AI models rely on scaling up neural networks, leading to unsustainable energy use and reduced interpretability.
- The new model mimics the human brain’s efficiency, operating on minimal power.
- Experiments validate the model’s effectiveness in handling complex tasks.
- The approach introduces new methods for integrating neuroscience into AI and optimizing AI performance.
Main AI News:
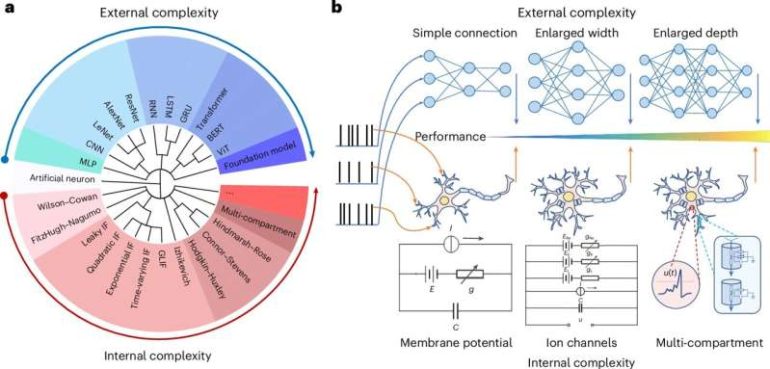
Chinese scientists have pioneered a groundbreaking brain-inspired network model focused on internal complexity to tackle the limitations of traditional AI frameworks, such as excessive computing resource demands, as reported by the Institute of Automation under the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
The research, featured in the journal Nature Computational Science, represents a significant leap toward the development of more versatile AI, aiming to imbue models with a broader and more general cognitive capability.
Currently, the predominant strategy for achieving general AI involves constructing increasingly larger, deeper, and more expansive neural networks, adhering to the “law of scale.” This approach, while promising, presents notable challenges, including unsustainable energy and computing resource consumption and a lack of transparency and interpretability, according to Li Guoqi, a researcher at the Institute of Automation.
In contrast, the human brain, with its approximately 100 billion neurons and nearly 1,000 trillion synaptic connections, operates on a mere 20 watts of power, thanks to each neuron’s rich and diverse internal structure. Drawing inspiration from these neural dynamics, scientists from the Institute of Automation, Tsinghua University, and Peking University have embraced an “internal complexity” approach to advance general intelligence.
Their experimental results affirm the effectiveness and robustness of this internal complexity model in addressing intricate tasks. This breakthrough introduces new methodologies and theoretical frameworks for integrating neuroscience’s dynamic principles into AI and offers practical pathways for enhancing AI models’ efficiency and performance.
Conclusion:
This breakthrough in brain-inspired AI represents a significant shift in the market, particularly in how AI models are developed and deployed. Focusing on internal complexity rather than merely scaling up existing models offers a more sustainable path forward, reducing energy consumption and enhancing model efficiency. This development could lead to a new era of AI applications, driving innovation across industries while potentially lowering operational costs and environmental impact. Companies that invest in integrating this advanced AI technology could gain a competitive edge, positioning themselves as leaders in the next generation of AI solutions.