- RadOnc-GPT, powered by Meta Llama 2, represents a paradigm shift in radiation oncology, enhancing decision-making precision and efficacy.
- Developed by Mayo Clinic, RadOnc-GPT leverages a vast dataset from patient records, ensuring both model robustness and data confidentiality.
- Dr. Wei Liu underscores the transformative potential of open-source LLMs like RadOnc-GPT in specialized healthcare domains.
- Initial deployment focuses on patient follow-up, with plans to introduce a chatbot for post-radiotherapy inquiries, relieving healthcare personnel.
- Future advancements may extend RadOnc-GPT’s capabilities, potentially incorporating the advanced features of Llama 3 for enhanced performance.
- Collaborative efforts with the University of Georgia underscore RadOnc-GPT’s specificity and clinical relevance, empowering healthcare providers.
- Open-source AI initiatives, exemplified by RadOnc-GPT, accelerate innovation in patient care and democratize access to cutting-edge technology.
Main AI News:
In the realm of artificial intelligence (AI), large language models (LLMs) have emerged as transformative assets across industries, reshaping operations with their adeptness at comprehending and generating human-like text. Among these, GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) models stand out, heralding a new era of efficiency and innovation. Yet, within the intricate landscape of medicine, precision and data reign supreme, nowhere more so than in radiation oncology, where patients’ lives hinge on the accuracy of treatments.
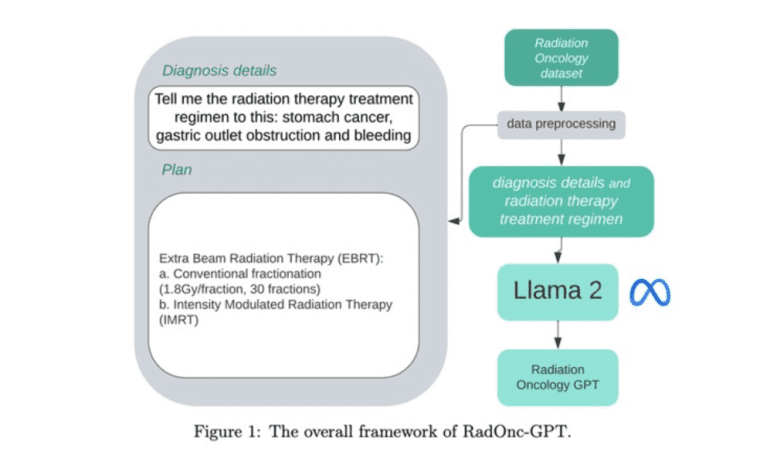
Enter RadOnc-GPT, Mayo Clinic’s formidable LLM fortified with Meta Llama 2 technology. This groundbreaking model holds promise in optimizing decision-making processes within radiation therapy, elevating precision and overall efficacy. Trained on a formidable dataset culled from patient records at Mayo Clinic’s radiation oncology department in Arizona, RadOnc-GPT embodies a convergence of cutting-edge technology and medical expertise. Notably, patient data confidentiality remained sacrosanct within the clinic’s network, with model refinement executed locally on a GPU server, powered by Llama 2 technology. All research endeavors involving RadOnc-GPT adhere to rigorous institutional review board protocols, ensuring ethical integrity.
Dr. Wei Liu, Professor of Radiation Oncology and Research Director of the Division of Medical Physics at Mayo Clinic in Arizona, underscores the transformative potential of finely tuned, open-source LLMs in specialized healthcare domains. The inaugural deployment of RadOnc-GPT focuses on patient follow-up, with plans to introduce a chatbot capable of addressing post-radiotherapy inquiries, thereby alleviating strain on healthcare personnel and fostering enhanced patient engagement.
Looking ahead, the horizon brims with possibilities for RadOnc-GPT. Future iterations may extend its purview to encompass diverse clinical functions, from prognostic modeling to treatment outcome forecasting. Dr. Liu hints at the team’s contemplation of leveraging the advanced capabilities of Llama 3, the latest addition to the Meta Llama series, to augment RadOnc-GPT’s performance further.
In the realm of healthcare, AI-driven tools wield transformative potential, expediting processes, unraveling complex datasets, and illuminating patterns imperceptible to the human eye. The collaborative efforts of Mayo Clinic and the University of Georgia underscore this ethos, with Llama 2 serving as the foundational framework for RadOnc-GPT. Fine-tuned to tasks ranging from treatment regimen generation to diagnostic insights, RadOnc-GPT epitomizes specificity and clinical relevance, empowering healthcare providers with actionable intelligence.
Crucially, the ethos of open-source AI pervades Mayo Clinic’s approach, facilitating the integration of state-of-the-art models into research endeavors. Dr. Liu emphasizes the dual benefits of this approach: accelerating innovation in patient care while democratizing access to cutting-edge technology. By championing open-source AI initiatives, Mayo Clinic paves the way for collective progress in medical science, transcending barriers of resource limitations and fostering a culture of inclusivity and collaboration.
Conclusion:
The introduction of RadOnc-GPT with Meta Llama heralds a paradigm shift in radiation oncology, promising heightened precision and efficiency in treatment decision-making. This innovation not only underscores Mayo Clinic’s commitment to advancing healthcare but also signals broader implications for the market, as open-source AI initiatives pave the way for collective progress and inclusivity in medical science.