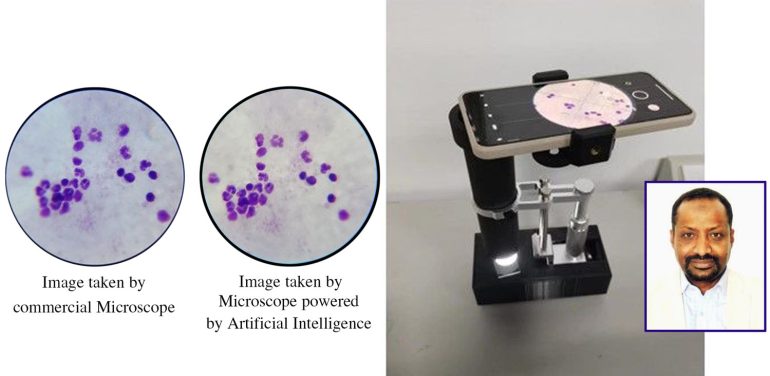
- Shantou University researchers unveil an AI-powered microscope for malaria diagnosis.
- Traditional diagnosis methods in resource-limited regions replaced by real-time algorithms.
- Professor Seedahmed Sharif Mahmoud leads the innovative project.
- Mahmoud’s expertise in electrical, electronic, and biomedical engineering crucial for success.
- AI-driven microscope poised to enhance healthcare outcomes in Africa and Asia.
Main AI News:
The unveiling of an AI-powered microscope by a team of researchers at Shantou University in China heralds a significant breakthrough in healthcare technology. Spearheaded by Professor Seedahmed Sharif Mahmoud and Professor Qiang Fang from the Department of Biomedical Engineering, this innovative device promises to revolutionize malaria diagnosis in resource-limited regions across Africa and Asia.
Traditionally, diagnosing malaria in these areas has been a daunting task, requiring skilled experts to manually count parasites and white blood cells. However, with the advent of this cutting-edge technology, the landscape is set to change. Powered by real-time algorithms and integrated with smartphones, the microscope can automatically detect malaria parasites and count white blood cells, offering a swift and precise diagnosis.
Professor Mahmoud, renowned for his expertise in electrical, electronic, and biomedical engineering, brings invaluable experience to the project. His pioneering work in signal processing for biomedical purposes and the development of optical fiber sensor devices has earned him recognition, including a Chinese patent and national and regional awards. Furthermore, his contributions to machine learning for perimeter intrusion detection systems have led to three international patents, cementing his status as a leader in the field.
Hailing from Sudan, Professor Mahmoud has been actively involved in numerous research projects, authored scientific papers and books, and acquired multiple patents, showcasing his dedication to advancing scientific knowledge. His visionary leadership continues to drive innovation in healthcare, with the AI-driven microscope poised to transform malaria diagnosis and improve outcomes for communities in need.
The unveiling of an AI-powered microscope by a team of researchers at Shantou University in China heralds a significant breakthrough in healthcare technology. Spearheaded by Professor Seedahmed Sharif Mahmoud and Professor Qiang Fang from the Department of Biomedical Engineering, this innovative device promises to revolutionize malaria diagnosis in resource-limited regions across Africa and Asia.
Traditionally, diagnosing malaria in these areas has been a daunting task, requiring skilled experts to manually count parasites and white blood cells. However, with the advent of this cutting-edge technology, the landscape is set to change. Powered by real-time algorithms and integrated with smartphones, the microscope can automatically detect malaria parasites and count white blood cells, offering a swift and precise diagnosis.
Professor Mahmoud, renowned for his expertise in electrical, electronic, and biomedical engineering, brings invaluable experience to the project. His pioneering work in signal processing for biomedical purposes and the development of optical fiber sensor devices has earned him recognition, including a Chinese patent and national and regional awards. Furthermore, his contributions to machine learning for perimeter intrusion detection systems have led to three international patents, cementing his status as a leader in the field.
Hailing from Sudan, Professor Mahmoud has been actively involved in numerous research projects, authored scientific papers and books, and acquired multiple patents, showcasing his dedication to advancing scientific knowledge. His visionary leadership continues to drive innovation in healthcare, with the AI-driven microscope poised to transform malaria diagnosis and improve outcomes for communities in need.
Conclusion:
The introduction of the AI-powered microscope for malaria diagnosis by Shantou University researchers, led by Professor Seedahmed Sharif Mahmoud, signifies a monumental advancement in healthcare technology. This innovation has the potential to revolutionize the market by providing swift and precise diagnosis in resource-limited regions, thereby improving healthcare outcomes for vulnerable communities.