TL;DR:
- Slingshot Aerospace employs AI to monitor satellite activities.
- Luch-2, Russia’s new spy satellite, exhibits behavior akin to its predecessor, raising concerns about space espionage.
- The company’s software detects Luch-2’s maneuvers and identifies abnormal behaviors among satellites.
- These insights are valuable for governments and commercial satellite operators concerned about space security.
- Although Luch-2 doesn’t trigger collision alerts, its presence raises security concerns.
- Luch-2 likely boasts advanced signals intelligence capabilities.
- Slingshot’s AI algorithm predicts satellite trajectories in real-time.
- Private companies like Slingshot contribute significantly to space domain awareness.
Main AI News:
In the realm of space surveillance, the significance of artificial intelligence (AI) cannot be overstated. Slingshot Aerospace, a leading player in space data analytics with a focus on spaceflight safety, has been at the forefront of harnessing AI to monitor satellite activities. Their recent findings have raised fresh concerns about espionage in space, particularly concerning Russia’s Luch-2 geostationary spy satellite.
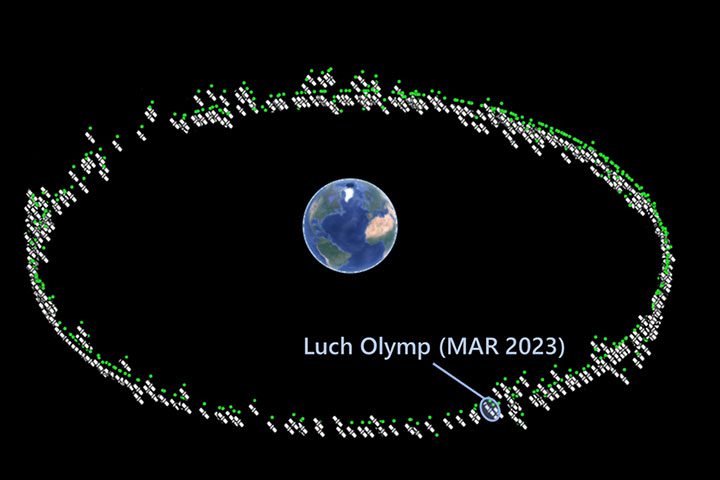
When Russia launched Luch-2, also known as Luch Olymp K-2, in March, it was expected to engage in signals intelligence-gathering missions, similar to its predecessor, Luch Olymp-K-1, which has been in orbit since 2014. Slingshot Aerospace’s space tracking software, designed to identify abnormal behaviors among satellites, has uncovered intriguing developments.
According to Slingshot, Luch-2 exhibited maneuvers reminiscent of those by Luch-1, which famously positioned itself between two Intelsat commercial communications satellites for five months in 2015, sparking international concern.
These maneuvers, detected starting from September 26, saw Luch-2 gradually drifting westward at a rate of approximately 1 degree per day before slowing down on October 2 to approach another “neighborhood” of GEO spacecraft.
Audrey Schaffer, Vice President of Strategy and Policy at Slingshot, revealed that their automated software for satellite tracking was not specifically monitoring Luch-2. Instead, they were actively seeking unusual behaviors. This approach provides valuable insights for both government and commercial satellite operators concerned about security in space.
While Luch-2’s actions did not trigger collision warnings from the U.S. Space Force, known as conjunction alerts, Schaffer emphasized that its presence could still pose security risks. Commercial communication satellite companies, in particular, may have concerns about potential eavesdropping by a Russian spy satellite.
Michael Clonts, Director of Space Domain Awareness Initiatives at Kratos Defense, pointed out that Luch-2 likely carries more advanced signals intelligence capabilities and operational techniques than its predecessor, thanks to a decade of technological advancements.
Slingshot’s space tracking software relies on a machine learning-based object profiling engine that consolidates data from multiple sources. Schaffer explained that their system not only tracked Luch-2’s drift but also predicted its trajectory, a challenging feat in real-time maneuver detection.
The algorithm is trained to distinguish between normal and abnormal behavior within specific orbits, automatically notifying operators when anomalies arise. This ability to swiftly identify deviations without the need for historical patterns sets Slingshot’s technology apart.
Schaffer, drawing from her experience as a former White House space policy official, emphasized the need to consider these satellite maneuvers when establishing international norms for responsible behavior in outer space. She noted that private companies like Slingshot Aerospace are now contributing to space domain awareness, broadening the scope beyond traditional military systems.
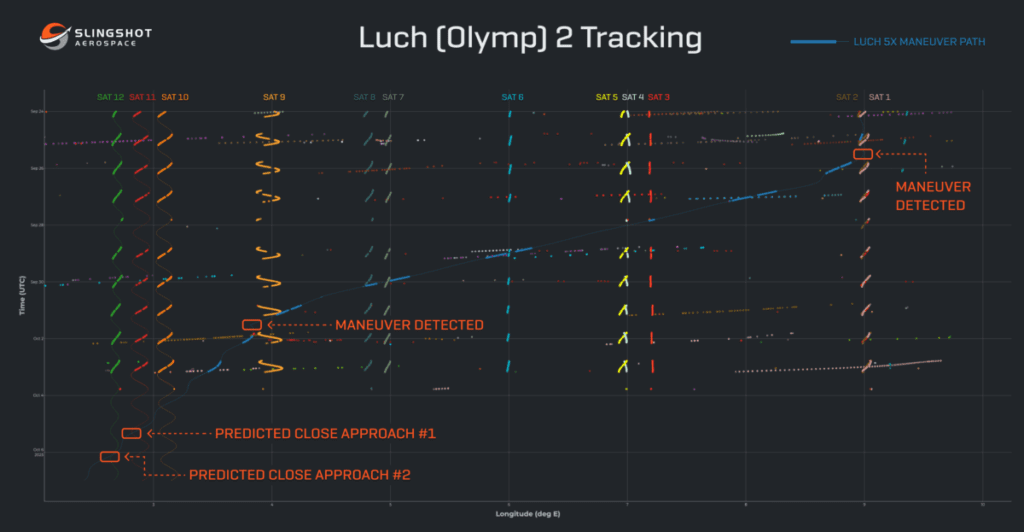
Image of the Slingshot Global Sensor Network’s optical tracking of Luch-2 as it drifted past a number of GEO satellites on its journey from ~9° East to ~3° East. Source: Slingshot Aerospace
Conclusion:
Slingshot Aerospace’s AI-driven satellite surveillance raises concerns about security in space. The detection of suspicious maneuvers by Russia’s Luch-2 highlights the importance of advanced technology in ensuring the safety and security of satellite operations. This development underscores the growing role of private entities in the evolving space market, where AI-driven solutions are becoming indispensable for space domain awareness.