TL;DR:
- Square introduces generative AI to help small businesses optimize their operations and drive sales.
- Retailers can use Square’s data to determine top-selling products and track employee performance.
- Generative AI provides real-time data visualization for informed decision-making.
- Square plans to deploy 30 generative AI applications this year and expand further in the future.
- The integration of generative AI sets Square apart from traditional banks, offering a competitive edge in data analytics.
- Square’s software manages customer relationships, staffing, and inventory, providing comprehensive business support.
- Generative AI assists in pricing, inventory management, and identifying best practices for businesses.
- The move reflects the intensifying competition major banks face from fintech disruptors in data analytics.
- Square’s marketing software is enhanced with generative AI, aiding businesses in targeting customers effectively.
- Despite economic challenges, Square’s customer base continues to grow, indicating strong market demand.
Main AI News:
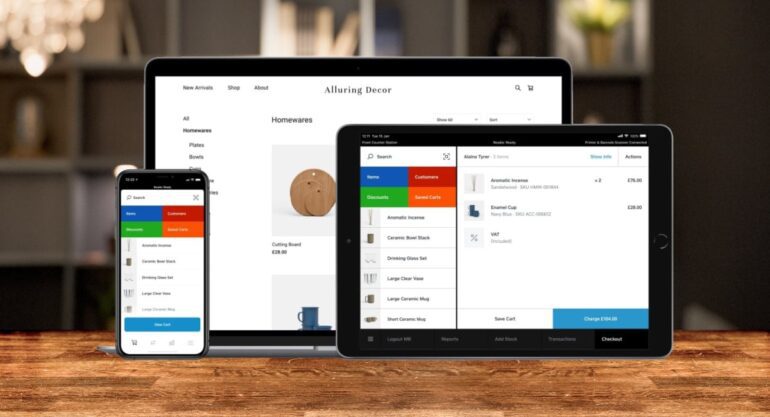
Square, the leading provider of payments and business software, is set to revolutionize the retail industry with its latest offering: generative artificial intelligence. This cutting-edge technology will empower small businesses to harness Square’s data and gain invaluable insights into their operations. By leveraging generative AI, merchants can identify top-selling products and determine the most productive employees, driving greater efficiency and profitability.
Imagine a local café that uses Square’s services. With generative AI at their disposal, they can simply input a query like, “How many cups of coffee have I sold on a Tuesday over the past 7 weeks?” In response, the system will generate an intuitive graphic, illustrating the exact numbers derived from the payment system’s real-time data. This unprecedented access to actionable information empowers retailers to make informed decisions that propel their businesses forward.
Square’s ambitious deployment of generative AI sets it apart from competitors like Macquarie and Commonwealth Bank, which have primarily focused on utilizing this technology to support call center operations. In contrast, Square is integrating generative AI tools directly into its software, enabling retailers to effortlessly inquire about product pricing, inventory, sales, and employee performance. This seamless integration streamlines business operations and unlocks new levels of efficiency.
“We view generative AI as an expert assistant,” explains Alyssa Henry, CEO of Square, during her visit to Sydney from San Francisco. “Its development is rapidly advancing, and customers are eager to embrace it. With improved AI capabilities, we are seamlessly integrating this technology into our product experience, ultimately saving sellers valuable time.“
This year, Square plans to deploy 30 applications for generative AI, following an internal hackathon in April that challenged software developers to harness the power of ChatGPT and similar large language models. Additionally, Square has exciting plans to unveil additional use cases in the coming year.
As a software company with access to rich data sets, Square is well-positioned to provide invaluable insights into business operations. By combining data with innovative technologies, Square empowers merchants to gain a deeper understanding of their businesses and optimize their performance. Whether it’s identifying top-selling products, analyzing sales velocity, or offering expert recommendations on employee performance, Square’s generative AI offers a powerful toolset for businesses seeking success.
Notably, Square’s comprehensive software also manages customer relationships and staffing, further enhancing its value proposition. Business owners can inquire about specific customer purchases or identify the highest-performing staff members, enabling targeted marketing campaigns or efficient rostering. Additionally, Square’s inventory management capabilities empower businesses to pinpoint best-selling products, facilitating seamless stock ordering processes.
Ms. Henry highlights Square’s unique ability to bridge the gap between data abundance and business analysis. “We possess a wealth of data, but many businesses struggle to analyze it effectively. By providing expert recommendations based on sales velocity, employee performance, and best practices, we equip businesses with the knowledge needed to optimize their operations, including setting aside funds for unforeseen circumstances,” she explains.
This strategic move by Square highlights the intensifying competition major banks face from offshore fintech disruptors in the realm of data analytics. Despite the challenging discretionary retail environment, Square’s customer base continues to expand, reaffirming its status as a market leader.
Furthermore, Square Loans, which competes with major banks by offering working capital to businesses, is experiencing steady growth. While Square does not disclose specific merchant numbers or lending figures, Ms. Henry emphasizes the company’s positive momentum in this domain.
Looking ahead, Square is exploring novel use cases for generative AI, leveraging anonymized, economy-wide data sets. For instance, users could input a query like, “What price is a business in my area selling this for?” This innovative feature would provide valuable insights into competitive pricing dynamics and economic conditions, enabling businesses to make informed pricing decisions.
Square’s accelerated rollout of generative AI comes in response to Macquarie’s recent announcement of an “AI-first approach” across its retail bank, with CBA also expressing deepening interest in this technology. Although both banks have utilized AI for customer insights and fraud detection, generative AI’s initial implementation will be limited to specific service areas relying on proprietary information and policies.
Square’s visionary approach extends beyond retail optimization. The company aims to leverage generative AI to enhance its marketing software, enabling businesses to target customers effectively. From assisting in selecting compelling visuals and crafting impactful email communications to suggesting language for responding to customer complaints, generative AI elevates Square’s marketing capabilities, ensuring businesses can make a lasting impression on their target audience.
Despite economic challenges, Square continues to witness rising “attach rates,” referring to its ability to cross-sell premium software alongside its foundational point-of-sale system. As times grow tougher, more businesses are turning to software solutions to optimize their operations, driving the demand for Square’s comprehensive suite of offerings.
Regarding Square’s acquisition of Afterpay in 2021, Ms. Henry emphasizes that all Square sellers can now accept Afterpay and the company is focused on introducing Square to Afterpay’s extensive merchant network. Additionally, Square envisions personalizing Afterpay’s “shop directory” to showcase a wider range of small businesses, thereby driving more referrals and supporting local enterprises.
Conclusion:
Square’s introduction of generative AI to the retail market signifies a transformative shift in business optimization. By leveraging real-time data and intuitive insights, retailers can make informed decisions, streamline operations, and drive profitability. This move positions Square as a leading player in the data analytics space, offering a comprehensive suite of software solutions that empower businesses to thrive in a challenging retail environment.