- Stanford introduces SUQL, a formal query language blending SQL semantics with NLP operators.
- SUQL enhances expressiveness, accuracy, and efficiency in querying hybrid knowledge sources.
- SUQL outperforms existing models in experiments on both synthetic and real-world data.
- Real-world applications demonstrate SUQL’s transformative potential in addressing complex queries.
- SUQL signifies a paradigm shift in data querying and integration, empowering users to unlock deeper insights.
Main AI News:
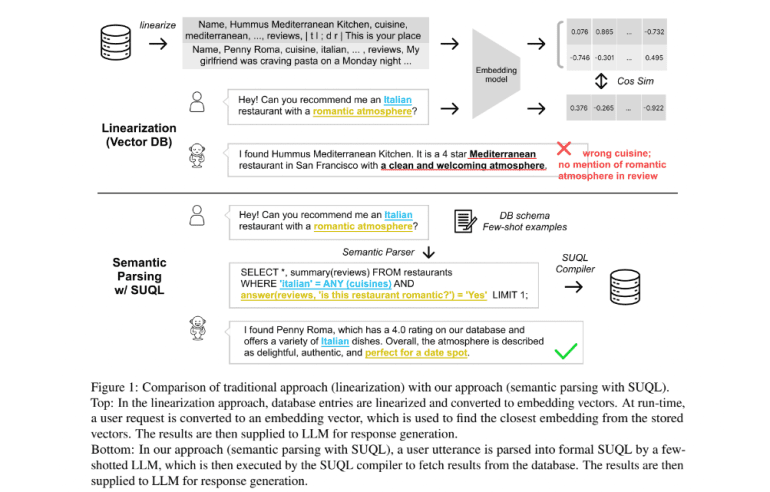
In the ever-evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, the synergy between Large Language Models (LLMs) and external data sources has emerged as a pivotal area of exploration. Stanford University researchers have recently introduced a revolutionary advancement in this domain with the unveiling of SUQL (Structured and Unstructured Query Language). This formal language promises to revolutionize the integration of structured and unstructured data, catering to the growing demand for nuanced and comprehensive data queries.
Traditionally, addressing queries spanning both structured and free-text data posed a significant challenge for existing systems. However, SUQL heralds a new era by seamlessly blending SQL semantics with NLP operators, empowering users to harness the full potential of hybrid knowledge sources. This innovative approach not only enhances expressiveness and precision but also ensures efficiency in query processing.
The design philosophy behind SUQL underscores its commitment to expressiveness, accuracy, and efficiency. By extending SQL with NLP operators such as SUMMARY and ANSWER, SUQL facilitates seamless navigation across diverse data sources. Furthermore, its compatibility with existing SQL compilers ensures ease of adoption, albeit with considerations for potential inefficiencies in naive implementations.
One of the hallmark features of SUQL is its ability to deliver superior performance across diverse datasets and use cases. In rigorous experiments conducted on both synthetic and real-world data, SUQL consistently outperformed existing models. For instance, in evaluations conducted on the HybridQA dataset, SUQL achieved an impressive 59.3% Exact Match (EM) and 68.3% F1 score, surpassing conventional approaches by a significant margin.
Real-world applications of SUQL further underscore its transformative potential. In experiments conducted on restaurant data sourced from Yelp.com, SUQL demonstrated remarkable turn accuracy in both single-turn and conversational queries. These findings highlight SUQL’s versatility and efficacy in addressing complex real-world scenarios, positioning it as a cornerstone technology in the realm of data integration and query processing.
Conclusion:
The introduction of SUQL by Stanford University signifies a significant advancement in the field of data integration and querying. With its ability to seamlessly bridge structured and unstructured data, SUQL not only enhances query precision and efficiency but also opens up new avenues for extracting insights and making informed decisions. This innovation is poised to reshape the market landscape, offering businesses unparalleled capabilities in leveraging their data assets to drive growth and innovation.