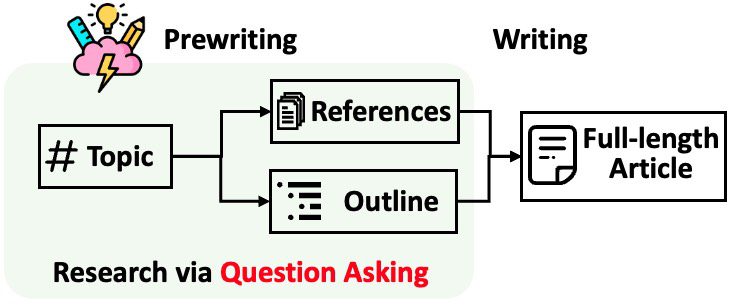
- STORM (Synthesis of Topic Outlines through Retrieval and Multi-perspective Question Asking) addresses challenges in generating comprehensive outlines for lengthy articles, like those on Wikipedia.
- Traditional methods often fail to capture the depth needed, resulting in poorly organized content.
- STORM integrates external information retrieval with language models to refine question generation and enhance article depth.
- It operates on the principles of leveraging diverse perspectives and iterative research to produce thorough outlines.
- Evaluation against human-written articles shows STORM’s superiority in outline quality, breadth, and organization.
- Challenges include addressing bias in sources and filtering out irrelevant information.
Main AI News:
STORM (Synthesis of Topic Outlines through Retrieval and Multi-perspective Question Asking) tackles the complex challenge of generating comprehensive outlines for lengthy articles, such as those found on Wikipedia. Traditional methods often fall short in capturing the full depth of topics, resulting in poorly organized or superficial content. The key issue lies in the ability of systems to formulate precise questions and gather information from diverse angles to craft well-rounded articles.
Existing solutions, like retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) models, attempt to bridge this gap by integrating external information retrieval with the capabilities of language models. However, these approaches frequently struggle with generating diverse and coherent questions. They may produce overly broad inquiries that miss critical details or fail to encompass multiple viewpoints, ultimately leading to articles that lack depth and coherence.
Researchers at Stanford have introduced STORM as a novel AI system designed to address these limitations. By enhancing the research capabilities of large language models, STORM excels in generating detailed and comprehensive outlines for long-form articles. The system operates on the premise that leveraging diverse perspectives leads to varied and insightful questions, and that deep, iterative research is essential for developing thorough outlines.
STORM’s methodology encompasses several pivotal stages:
- Perspective Discovery: Retrieving and analyzing Wikipedia articles related to the topic to uncover diverse viewpoints.
- Question Generation: Formulating inquiries from specific perspectives, fostering a wide range of investigative angles. These questions undergo refinement through multi-turn simulations, simulating dialogues grounded in retrieved internet data.
- Outline Creation: Constructing a structured outline based on collected information and the system’s internal knowledge.
The efficacy of STORM has been rigorously evaluated using the FreshWiki dataset, which features recent, high-quality Wikipedia articles. Evaluation metrics assess outline quality, breadth, organization, and relevance relative to human-authored articles. Both automated assessments and human evaluations consistently demonstrate STORM’s superiority over traditional RAG models, particularly in terms of article depth and structure. This underscores STORM’s ability to generate thorough and well-organized outlines.
Despite its advancements, STORM faces challenges such as source bias and the potential inclusion of irrelevant facts. Addressing these issues will be pivotal in further enhancing the system’s performance. Nevertheless, STORM stands as a robust solution for automating the initial stages of long-form article creation. It underscores the significance of multi-perspective and iterative research in producing detailed and coherent article outlines, setting a new benchmark for grounded content generation.
Conclusion:
The introduction of STORM represents a significant advancement in automating the creation of detailed long-form article outlines. Its ability to improve content depth and organization underscores its potential to set a new standard in content generation, particularly for industries reliant on informative and well-structured written materials.