TL;DR:
- Synthesia, a London-based startup, launches an AI video assistant to transform text-based sources into synthetic videos quickly.
- The tool streamlines the video creation process for enterprise teams by eliminating manual script writing and design efforts.
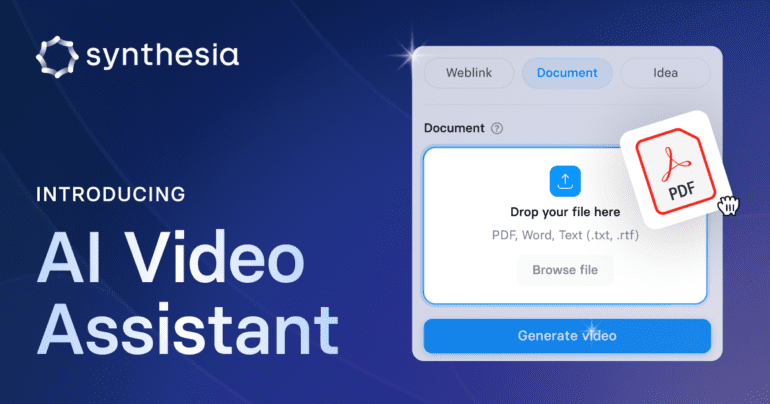
- Users input source material, select templates, and receive a video output within minutes.
- The AI video assistant aims to bridge the gap between text-based content and video delivery, improving retention rates.
- While Synthesia has attracted significant interest from customers, there is a 4,500-word limit on its capabilities.
- Despite concerns about AI-generated videos and deepfakes, Synthesia has experienced steady growth and secured funding, with clients including Zoom.
Main AI News:
London-based startup Synthesia, known for its pioneering work in helping enterprises produce professional AI videos, has just launched a game-changing AI video assistant. This innovative tool has the remarkable ability to transform text-based sources into fully-fledged synthetic videos in a matter of minutes. Available immediately for paying customers, the AI video assistant is a groundbreaking addition to Synthesia’s existing suite of offerings, enabling enterprise teams to effortlessly generate videos for both internal and external purposes.
This latest advancement in AI technology marks a significant stride forward in content delivery capabilities. However, it also raises eyebrows in light of the increasing concerns surrounding AI-generated videos and deepfakes, and how they can be harnessed to manipulate the perception of actors and politicians among internet users.
The Synthesia AI video assistant builds upon the foundation laid by the company since its inception in 2017. A collaborative effort of AI researchers and entrepreneurs from renowned institutions like UCL, Stanford, TUM, and Cambridge, Synthesia has provided a comprehensive platform allowing users to craft custom AI voices and lifelike AI avatars. These digital assets can be seamlessly integrated into studio-quality videos.
While Synthesia’s offerings had garnered significant traction in enterprise settings, the video creation process still required a certain level of effort. Tasks like manual script writing or utilizing AI for script creation, and the meticulous design of video layouts by selecting avatars, languages, and brand elements remained part of the workflow.
With the introduction of the AI video assistant, Synthesia has revolutionized this entire process. Users are now freed from these labor-intensive tasks. All that’s needed is to input the source material, which can be sourced from websites, text files, word documents, PDFs, or even conceptual ideas. Users then select a template specifying the video’s objective, the number of scenes, and the desired language and tone of the featured speaker.
Sundar Solai, the product manager responsible for developing the assistant at Synthesia, explains, “The AI Video Assistant employs generative AI to amalgamate the user’s source material with their objectives, target audience, and other relevant characteristics. Large language models process these inputs, generating both a script and pertinent scene layouts based on the selected template.”
This entire process takes mere minutes, culminating in the conversion of the output into a fully-fledged video. Should the initial script not meet the user’s expectations, adjustments can be made promptly, affording users the ability to refine their content to perfection.
Enhancing the Content Delivery Experience
Studies have shown that people retain up to 95% of a message when presented via video compared to a mere 10% when delivered as text. Despite this, many organizations continue to rely on dense handbooks and PDFs for disseminating valuable content to their employees and clients. Synthesia’s AI video assistant seeks to bridge this gap, allowing individuals within any organization, with the appropriate access, to transform disorganized, text-based information into high-quality videos.
Solai reports that they have been conducting extensive testing of the assistant, noting substantial interest from customers. However, he did not disclose the number of companies involved in the initial trials or the specific applications for which they utilized the assistant. He added, “In addition to enabling users to create videos more efficiently, this feature has expanded Synthesia’s ability to democratize video creation, making it accessible to an even broader audience, including those with limited or no prior video editing experience.“
Despite its immense potential for boosting enterprise content delivery efforts, it’s crucial to be aware of the AI video assistant’s current limitations. Whether handling a text file or a web link, Synthesia specifies that there is presently a 4,500-word limit on the assistant’s capabilities.
Steady Growth Amid Deepfake Concerns
While debates continue within regulatory bodies and the broader community about the risks posed by AI video and voice manipulation tools, Synthesia has continued to make significant strides, focusing on enterprise users. The company, with a workforce of 300 employees, successfully secured $90 million in funding in June 2023 and now boasts more than 55,000 businesses as clients, including half of the Fortune 100 companies. Notably, video communication service Zoom is one of Synthesia’s satisfied customers, having achieved a 90% increase in video creation speed for sales and training purposes.
Alexandru Voica, Head of Corporate Affairs and Policy at Synthesia, highlighted Zoom’s experience, stating, “This means Zoom’s subject matter experts no longer need to record themselves, freeing up 15-20 hours of their time each month that they can allocate to other job-related tasks. Zoom has also realized monthly cost savings of $1,000-$1,500 per employee, previously spent on creating training videos.”
Voica also revealed that Synthesia is actively working on improving the platform’s speed and advancing the next generation of its avatar technology. These enhancements will enable more expressive avatars with natural movements, enhanced voices, and greater customization options, bringing the platform’s AI-generated videos one step closer to achieving lifelike realism. In the competitive landscape of AI video production, Synthesia faces rivals such as Deepbrain AI, Rephrase, and HeyGen.
Conclusion:
Synthesia’s AI video assistant represents a significant advancement in content creation, catering to enterprises looking to improve their video delivery efforts. While concerns regarding AI-generated content persist, Synthesia’s success and continued innovation highlight the growing demand for such solutions in the market. As the company refines its technology, it remains poised to further disrupt the content creation landscape, potentially enticing more businesses to adopt AI-driven video production.