TL;DR:
- Language as a potent tool in human interaction, transcending sight and sound.
- Language’s role in enhancing sensory modes and conveying maximum information.
- Multi-modal modeling’s efforts to intertwine language with various senses.
- Introduction of “Fine-grained Audible Video Description” (FAVD) task for detailed video narration.
- FAVD’s focus is on gradual information disclosure, enriching video essence through language.
- Inclusion of audio descriptions in FAVD, enhancing holistic content depiction.
- Fine-grained Audible Video Description Benchmark (FAVDBench) with rich dataset.
- Novel metrics: EntityScore and AudioScore for evaluating FAVD task.
- Model evolution from visual-language to audio-visual-language transformer (AVLFormer).
- Adaptation of visual and audio encoders for multi-modal token synthesis.
Main AI News:
In the realm of human interaction, language stands as the supreme conduit, transcending the realms of sight and sound. Beyond being a mere companion to these faculties, language emerges as a potent instrument for information dissemination. Think voice-guided navigation leading us unerringly to a destination or the descriptive audio painting vivid cinematic experiences for the visually impaired. These instances underscore language’s role in enriching sensory modes and its ability to convey maximal information across diverse modalities.
Today’s pursuit of multi-modal modeling endeavors to forge intricate ties between language and various senses. It spans tasks like captioning images or videos, transmuting visual content into textual representations, and employing text-guided manipulation of visuals, among others. CodiumAI, catering to busy developers, presents a novel avenue for generating purposeful tests, streamlining the process.
However, amidst these endeavors, language often serves as a supplement to information from other sensory streams. This tends to leave gaps in comprehensively capturing the intricate exchange of information between different sensory realms. The emphasis remains largely on rudimentary linguistic components, often confined to one-sentence captions.
Such brevity confines these captions to describe prominent elements and actions, inevitably leading to limited information conveyance compared to the richness offered by other sensory channels. This discord becomes pronounced when translating information from diverse sensory dimensions into language.
Within this research, language emerges as the key to unlocking multi-modal modeling’s potential. Introducing the “Fine-grained Audible Video Description” (FAVD) task, researchers depart from conventional video captioning. While brief video captions tend to focus on primary aspects, FAVD challenges models to emulate human narration. It encourages a gradual divulgence of information, commencing with concise summaries and progressively incorporating intricate details. This approach imprints a more substantial portion of video essence within the linguistic structure.
Given videos’ fusion of visual and auditory cues, the FAVD task ingeniously incorporates audio descriptions, enhancing the holistic depiction. To operationalize this endeavor, a benchmark christened Fine-grained Audible Video Description Benchmark (FAVDBench) comes to the fore. This repository comprises 11,000+ video clips spanning 70 real-life categories, culled from YouTube. Annotations comprise succinct one-liners summarizing content, succeeded by 4-6 elaborate sentences detailing visual attributes and 1-2 sentences concerning audio aspects. A treasure trove of comprehensive data takes shape.
Two innovative metrics come to fruition to assess the FAVD task’s efficacy. “EntityScore” quantifies the migration of information from videos to descriptions by evaluating the inclusiveness of entities within visual depictions. “AudioScore,” the second metric, gauges audio description quality within the feature landscape of a pre-trained audio-visual-language model.
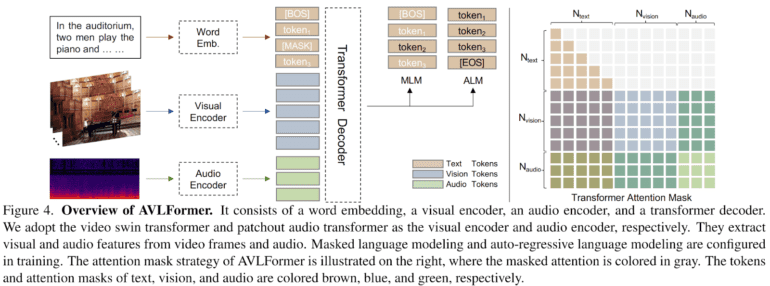
The research lays the foundation with a novel model for the introduced task. This model builds upon a well-established end-to-end video captioning framework, bolstered by an added audio dimension. Extending from a visual-language transformer, the model evolves into an audio-visual-language transformer (AVLFormer).
Visual and audio encoders undergo tailoring for processing video clips and audio, respectively. This amalgamation yields multi-modal tokens. The video encoder leverages the video swin transformer, while the audio encoder employs the patchout audio transformer. Extracting visual and audio features from respective sources, these components play a pivotal role. Training incorporates additional components like masked language modeling and auto-regressive language modeling. Drawing inspiration from prior video captioning models, AVLFormer ingests textual descriptions as input. Employing a word tokenizer and linear embedding, textual information adopts a specific format. The transformer processes this amalgamated information, yielding finely detailed video descriptions.

Source: Marktechpost Media Inc.
Conclusion:
The transformative integration of language into multi-modal video narration, exemplified by the FAVD task and AVLFormer model, marks a significant advancement. This innovation fosters more immersive and comprehensive content experiences, catering to diverse sensory perceptions. The market can anticipate an evolution in content creation, personalized experiences, and accessibility solutions, driven by the newfound potential of AI-driven narrative enhancement.