TL;DR:
- Uber Eats is introducing a chatbot feature to improve customer experience.
- Initially, the AI assistant will help users find restaurant deals and reorder favorite dishes.
- Future capabilities include meal planning, grocery item discounts, and ingredient ordering.
- Uber aims to retain customers and increase platform spending with this innovation.
- The chatbot will be powered by Google’s PaLM 2 LLM and leverage extensive merchant data.
- Users can make specific requests via chat, simplifying the ordering process.
- Other food delivery apps like DoorDash and Instacart are also exploring AI integration.
Main AI News:
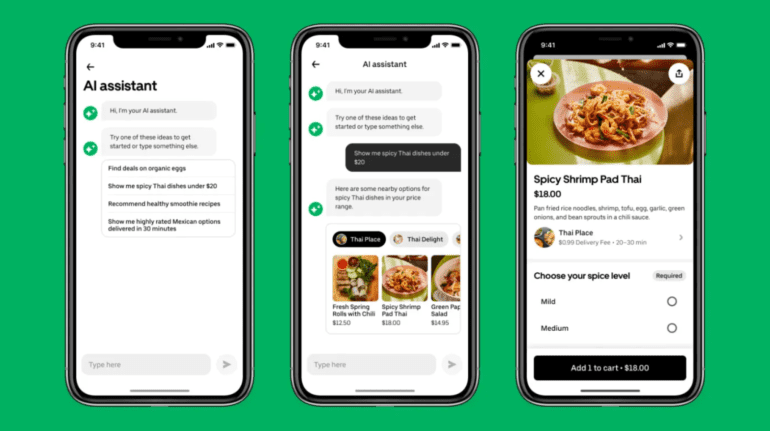
In a bid to enhance customer experience and retain its user base, Uber Eats has unveiled its plan to introduce a groundbreaking chatbot function later this year. This AI-driven assistant will cater to customers in the United States, United Kingdom, Australia, and Canada. Initially, the chatbot, dubbed the “AI assistant,” will assist users in discovering enticing restaurant deals and streamlining the process of reordering their favorite dishes through the Uber Eats app.
As part of its evolving capabilities, this AI assistant will soon extend its services to help users with meal planning, identifying discounts on grocery items, and even facilitating the ordering of ingredients required for various recipes, according to Uber’s official statement.
Uber has been on an innovation spree in recent years, introducing new products and features designed not only to attract fresh clientele but also to retain its existing customer base. With a goal to encourage increased spending on its platform, Uber is seizing the opportunity to deploy an AI assistant, which could prove to be a game-changer in the world of food delivery.
The introduction of this chatbot signifies Uber’s foray into the realm of artificial intelligence, a space that is currently bustling with activity as companies across various industries scramble to incorporate the power of large language models (LLMs) post the ChatGPT era. More than just an addition to their platform, this AI assistant could be Uber’s strategic move to engage users through conversational AI, potentially yielding higher conversion rates compared to the company’s newly implemented and occasionally intrusive in-app advertisements.
Powering this AI assistant is Google’s PaLM 2 LLM, supported by insights derived from Google’s vast catalog comprising over 900,000 merchants. The launch of PaLM 2 was a highlight at Google’s I/O developer conference in May, marking a significant milestone in the evolution of language models. This LLM, Bard, is set to be Google’s answer to the ChatGPT phenomenon.
Through a chat-based interface, customers will have the ability to make specific requests, such as locating spicy vegetarian Thai dishes, discovering trending Mexican restaurants in New York City, or finding dumplings priced under $15 that can be delivered within 30 minutes. The chatbot will promptly respond with a curated list of stores and dishes that align with the customer’s preferences.
In demonstration, the chatbot was prompted with the request, “show me popular picnic snacks.” In response, it provided recommendations for picnic essentials, including items like Gouda cheese and chocolate chip cookies available at a nearby supermarket. Upon the customer’s follow-up request for organic options, the chatbot efficiently suggested fresh fruits like apples, berries, and grapes. It then offered additional alternatives to cater to the customer’s preference for healthier snack choices, ultimately leading to the selection of a trail mix from the local supermarket, which was seamlessly added to the customer’s cart.
Uber asserts that this chatbot feature will not only save customers valuable time but also simplify the ordering process by eliminating the need to navigate through menus and browse across various stores.
Notably, Uber is not the only player in the food delivery industry exploring the integration of AI into its platform. DoorDash, for instance, recently launched an AI-powered voice ordering technology, which handles restaurant orders on behalf of customers by responding to calls. DoorDash is also actively developing its own chatbot to further elevate the user experience.
Instacart has also introduced a similar tool, driven by ChatGPT technology, known as “Ask Instacart.” This innovative search tool serves up personalized recommendations to customers, further contributing to the growing influence of AI in the world of food delivery.
Conclusion:
Uber Eats’ introduction of an AI chatbot marks a significant step in enhancing the food delivery market. This innovation is poised to improve user engagement, streamline the ordering process, and potentially drive higher conversions. As other major players like DoorDash and Instacart follow suit, the market is evolving towards a more personalized and efficient customer experience, underlining the increasing influence of AI in the industry.