TL;DR:
- Unified-IO 2 is an autoregressive multimodal AI model capable of processing and generating text, images, audio, and video.
- Developed by researchers from the Allen Institute for AI, the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, and the University of Washington.
- It employs a unique architecture that converts diverse data types into a unified semantic space.
- Methodology includes byte-pair encoding for text, a pre-trained Vision Transformer for images, and an Audio Spectrogram Transformer for audio.
- Achieved outstanding performance across 35+ datasets, excelling in tasks like keypoint estimation and image generation.
- Presents a significant advancement in AI capabilities, particularly in the integration of multimodal data.
Main AI News:
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, the integration of multimodal data has emerged as a game-changer. While traditional AI models excelled in single-mode tasks, the real world often demands the fusion of text, images, audio, and video. Addressing this complexity, “Unified-IO 2,” developed by a collaboration of researchers from the Allen Institute for AI, the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, and the University of Washington, represents a monumental leap in AI capabilities.
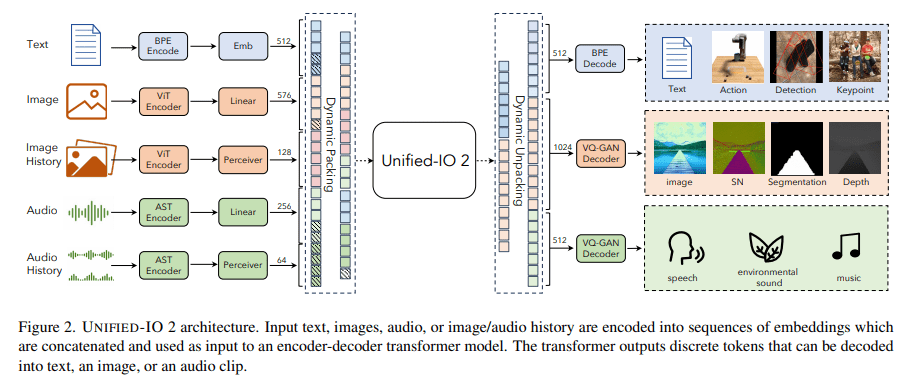
Unified-IO 2 transcends its predecessors by being an autoregressive multimodal model, capable of comprehending and generating a wide spectrum of data types, including text, images, audio, and video. What sets it apart is its unique architecture, built upon a single encoder-decoder transformer model that can seamlessly convert diverse inputs into a unified semantic space. This innovative approach empowers the model to process multiple data types concurrently, surmounting the limitations of earlier models.
The methodology underpinning Unified-IO 2 is as sophisticated as it is pioneering. It leverages a shared representation space to encode various inputs and outputs, utilizing byte-pair encoding for text and special tokens for encoding sparse structures such as bounding boxes and key points. Images undergo encoding through a pre-trained Vision Transformer, with a subsequent transformation into embeddings suitable for the transformer input. Audio data follows a similar path, being processed into spectrograms and encoded using an Audio Spectrogram Transformer. The model further incorporates dynamic packing and a multimodal mixture of denoisers’ objectives, enhancing its efficiency and effectiveness in handling multimodal signals.
Unified-IO 2’s performance is nothing short of impressive. Across an extensive evaluation involving more than 35 datasets, it establishes a new benchmark in the GRIT evaluation, demonstrating excellence in tasks like keypoint estimation and surface normal estimation. In the domain of vision and language tasks, it either matches or surpasses many of the recently proposed Vision-Language Models. Notably, its prowess in image generation stands out, outperforming its closest competitors in terms of faithfulness to prompts. The model also adeptly generates audio from images or text, underscoring its versatility across a broad spectrum of capabilities.
Unified-IO 2 has the potential to reshape the AI landscape, offering businesses a powerful tool for harnessing the full potential of multimodal data. Its ability to seamlessly integrate and generate text, images, audio, and video positions it as a transformative force in the world of artificial intelligence. With Unified-IO 2, businesses can unlock new possibilities and drive innovation in their operations.
Source: Marktechpost Media Inc.
Conclusion:
Unified-IO 2 signifies a significant leap in AI capabilities with its capacity to handle and generate multimodal data. Businesses can leverage this technology to unlock innovative possibilities and gain a competitive edge in the evolving market for AI-driven solutions. Unified-IO 2’s prowess in various tasks makes it a valuable asset for businesses seeking to harness the power of AI across different data types, ultimately transforming the landscape of AI applications.

