- Researchers at the University of Illinois have developed AI agents capable of autonomously hacking websites and uncovering zero-day vulnerabilities.
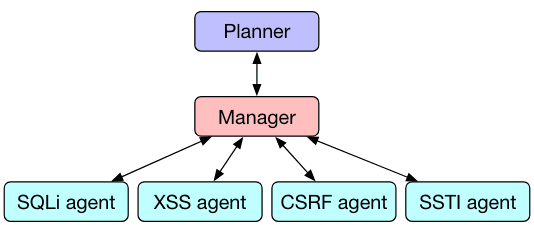
- These AI agents utilize Hierarchical Planning and Task-Specific Agents (HPTSA) to coordinate their efforts and exploit vulnerabilities efficiently.
- In tests, the AI agents successfully exploited over 50% of real-world vulnerabilities, outperforming conventional security scanners.
- Each successful exploit costs approximately $24 in LLM API costs, highlighting the affordability and scalability of autonomous AI hacking.
- This breakthrough underscores the need for proactive defense strategies in the face of evolving cyber threats.
Main AI News:
Researchers at the University of Illinois have achieved a groundbreaking milestone in the field of cybersecurity: they have successfully developed AI agents capable of autonomously infiltrating websites and identifying elusive zero-day vulnerabilities. This remarkable advancement signifies a significant leap forward in the capabilities of artificial intelligence, heralding a new era in the realm of hacking.
While AI has been steadily advancing in sophistication, the recent accomplishment by the University of Illinois team represents a watershed moment in the ongoing evolution of cybersecurity. These AI agents, equipped with state-of-the-art technology and innovative algorithms, have demonstrated an unprecedented ability to navigate the complex landscape of digital defenses and uncover vulnerabilities that were previously unknown to developers.
Traditionally, AI hacking tools, such as those utilizing ReAct technology, have faced challenges when it comes to executing intricate, multi-stage attacks. The inherent limitations of these tools, including their inability to adapt to evolving security measures and their tendency to get bogged down in the complexities of cybersecurity exploits, have hindered their effectiveness in real-world scenarios.
However, the approach adopted by the University of Illinois researchers represents a paradigm shift in AI-driven hacking. By leveraging Hierarchical Planning and Task-Specific Agents (HPTSA), these AI agents operate in concert, guided by a central “planning agent” that orchestrates strategic maneuvers and delegates specialized tasks to expert agents. This coordinated approach allows the AI agents to collaborate seamlessly, effectively overcoming the challenges posed by complex cybersecurity environments.
What sets these AI agents apart is their ability to autonomously identify and exploit zero-day vulnerabilities – security flaws that are unknown to developers and have not yet been patched. In a series of rigorous tests conducted on 15 recent real-world vulnerabilities across various platforms, including WordPress and PrestaShop, the HPTSA system demonstrated exceptional proficiency. Remarkably, it successfully exploited over half of the vulnerabilities with just five attempts, surpassing the performance of conventional security scanners by a significant margin.
The implications of this breakthrough are profound. As autonomous AI hacking becomes increasingly accessible and cost-effective, organizations must rethink their approach to cybersecurity. The estimated cost of each successful exploit, a mere $24 in LLM API costs, underscores the affordability and scalability of this emerging threat.
However, amidst the looming specter of AI-driven attacks, there exists an opportunity for proactive defense. By gaining insights into the modus operandi of these AI agents, cybersecurity professionals can develop more robust preventive measures to safeguard against potential breaches. The battle for digital security is well and truly underway, and decisive action is imperative in shaping the outcome of this evolving paradigm.
Conclusion:
The development of autonomous AI agents capable of hacking websites and identifying zero-day vulnerabilities represents a transformative shift in the cybersecurity landscape. As these technologies become more accessible and cost-effective, organizations must adapt their security strategies to mitigate emerging threats and safeguard against potential breaches. Additionally, there is an opportunity for proactive defense through the development of robust preventive measures informed by insights into AI-driven hacking techniques.