- Cybersecurity experts uncover LLMjacking, targeting cloud-hosted large language model (LLM) services.
- Attackers exploit stolen cloud credentials to gain access, aiming to sell access to other threat actors.
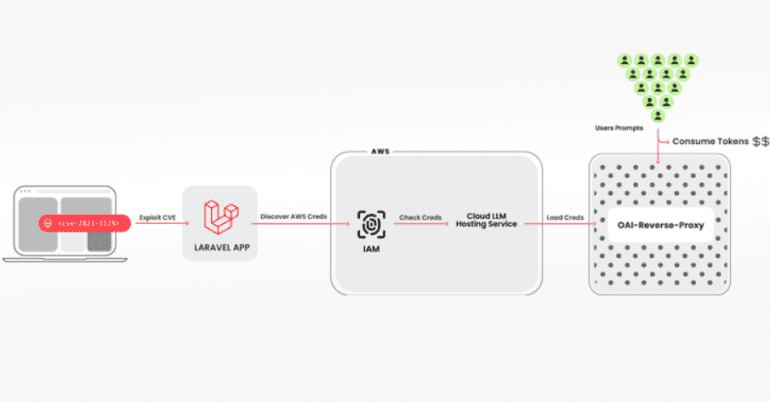
- Vulnerable systems, like those running Laravel Framework, are breached to obtain Amazon Web Services (AWS) credentials.
- An open-source Python script is utilized to validate keys across platforms like Anthropic, AWS, Google Cloud, and OpenAI.
- Attackers employ a reverse proxy tool to hide credentials while providing access to compromised accounts.
- Focus shifts from prompt injections and model poisoning to monetizing LLM access, costing victims up to $46,000 per day.
- Organizations advised to enhance logging, monitor cloud activity, and strengthen vulnerability management.
Main AI News:
Cybersecurity analysts have stumbled upon an innovative assault leveraging purloined cloud credentials to target cloud-hosted extensive language model (LLM) services, aiming to vend access to other malevolent actors. Termed LLMjacking by the Sysdig Threat Research Team, this maneuver is causing ripples across the cybersecurity landscape.
Alessandro Brucato, a security researcher, elucidated, “After securing the initial access, they extracted cloud credentials and infiltrated the cloud environment, setting their sights on local LLM models hosted by cloud providers. Specifically, they zeroed in on a local Claude (v2/v3) LLM model from Anthropic.”
The infiltration process involves breaching a system housing a vulnerable version of the Laravel Framework, followed by commandeering Amazon Web Services (AWS) credentials to reach the LLM services. The attackers wield an array of tools, including an open-source Python script, to vet and authenticate keys across various platforms like Anthropic, AWS Bedrock, Google Cloud Vertex AI, Mistral, and OpenAI.
Brucato expounded, “During the validation phase, no genuine LLM queries were executed. Instead, they conducted a cursory check to discern the capabilities of the credentials and any imposed limitations.” The keychecker tool seamlessly integrates with oai-reverse-proxy, enabling threat actors to offer access to compromised accounts while shielding the underlying credentials from exposure.
“If the malefactors intend to amass a repository of valuable credentials and peddle access to accessible LLM models, employing a reverse proxy facilitates the monetization process,” Brucato emphasized. Moreover, the assailants have exhibited a penchant for probing logging settings, likely in a bid to evade detection while leveraging compromised credentials.
This modus operandi represents a departure from conventional attacks centered on prompt injections and model contamination, affording perpetrators the opportunity to capitalize on LLM access while the cloud account owner bears the brunt of the financial burden unknowingly.
Sysdig sounded the alarm, asserting that such an incursion could result in staggering LLM consumption costs exceeding $46,000 per day for the victim. “Utilizing LLM services can exact a hefty toll, contingent upon the model and token volume,” Brucato cautioned. “By maximizing quota thresholds, attackers can incapacitate the compromised organization’s legitimate usage of models, thereby disrupting business continuity.”
Organizations are urged to bolster their defenses by activating comprehensive logging mechanisms and diligently scrutinizing cloud logs for signs of anomalous or unauthorized behavior. Additionally, robust vulnerability management protocols should be instituted to thwart initial access attempts.
Conclusion:
The emergence of the LLMjacking scheme underscores the evolving sophistication of cyber threats targeting cloud-hosted AI models. With attackers pivoting towards monetization strategies, businesses must fortify their cybersecurity defenses to safeguard against potential financial and operational disruptions. Proactive measures such as comprehensive logging, vigilant monitoring, and robust vulnerability management are imperative to mitigate the risks posed by such clandestine incursions.