TL;DR:
- ViLa is a cutting-edge AI methodology utilizing GPT-4V for long-horizon robotic task planning.
- Developed by researchers at Tsinghua University and Shanghai AI Laboratory, ViLa integrates vision and language understanding.
- It excels in open-world manipulation tasks, even in zero-shot scenarios.
- The study focuses on the application of vision-language models (VLMs) for robotics and visual question answering.
- ViLa stands out for its adaptability, encoding commonsense knowledge and actionable steps for robots.
- It outperforms existing LLM-based planners in spatial layouts, object attributes, and multimodal goals.
Main AI News:
In the realm of robotic task planning, achieving unparalleled performance has been a longstanding challenge. Researchers hailing from Tsinghua University, Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, and Shanghai Qi Zhi Institute have risen to this challenge with the introduction of Vision-Language Planning (ViLa). ViLa seamlessly amalgamates the realms of vision and language comprehension, leveraging the formidable capabilities of GPT-4V to encode profound semantic knowledge and tackle intricate planning conundrums, even within the uncharted territory of zero-shot scenarios. This pioneering methodology opens the door to extraordinary feats in the domain of open-world manipulation tasks.
The study delves into the continuous evolution of Large Language Models (LLMs) and the burgeoning interest in the expansion of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) for multifaceted applications, ranging from visual question answering to robotics. It meticulously categorizes the application of pre-trained models into three distinct domains: vision, language, and vision-language models. The core focus revolves around harnessing the visually anchored attributes of VLMs to surmount the intricate challenges associated with long-term planning in robotics, effectively reshaping the landscape of high-level planning with an infusion of common-sense knowledge. ViLa, fortified by the unparalleled capabilities of GPT-4V, emerges as a standout performer in the realm of open-world manipulation tasks, underscoring its effectiveness in everyday operations sans the need for additional training data or in-context examples.
Scene-aware task planning, a quintessential hallmark of human intelligence, hinges on contextual comprehension and adaptability. While LLMs have proven their mettle in encoding semantic knowledge for intricate task planning, their Achilles’ heel lies in the prerequisite of grounding in the physical world for robotic applications. In addressing this critical limitation, Robotic ViLa emerges as a groundbreaking approach, seamlessly integrating vision and language processing. Diverging from conventional LLM-based methodologies, ViLa emboldens VLMs to craft actionable directives grounded in visual cues and high-level linguistic instructions. The overarching objective is the creation of embodied agents, akin to robots, endowed with a human-like adaptability and an aptitude for long-term task planning across diverse scenarios.
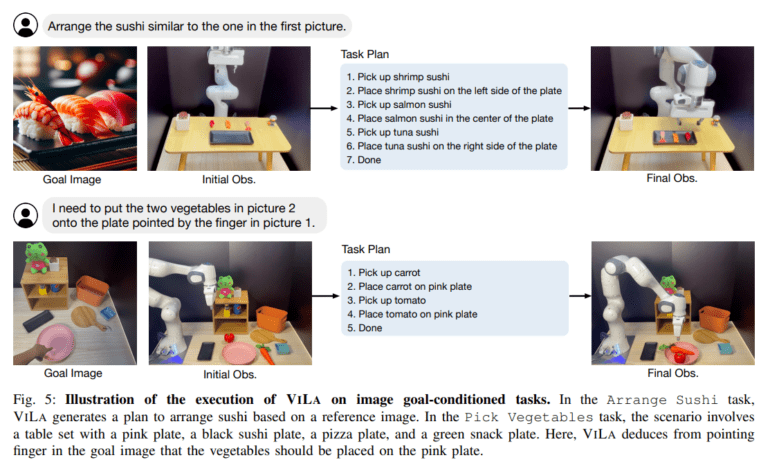
ViLa, in essence, embodies a planning methodology that harnesses the prowess of vision-language models as the architects of robotic planning. It intricately weaves vision into the fabric of reasoning, tapping into a reservoir of common-sense knowledge deeply rooted in the visual domain. At the heart of this technological marvel is GPT-4V(ision), a pre-trained vision-language model that serves as the vanguard in the realm of task planning. Rigorous evaluations, conducted in both real-world and simulated environments, unequivocally demonstrate ViLa’s supremacy over incumbent LLM-based planners in the domain of diverse open-world manipulation tasks. Its distinctive attributes encompass deft spatial layout management, meticulous consideration of object attributes, and the seamless integration of multimodal goal processing.
ViLa unequivocally outshines existing LLM-based planners when it comes to open-world manipulation tasks. It excels in realms such as spatial layout management, object attribute handling, and the intricate orchestration of multimodal goals. Empowered by the indomitable capabilities of GPT-4V, ViLa emerges as a panacea for complex planning dilemmas, even operating in a zero-shot mode. With ViLa at the helm, errors are significantly reduced, and it seamlessly accomplishes tasks that demand astute spatial arrangements, a profound understanding of object attributes, and an innate grasp of common-sense knowledge.
Conclusion:
ViLa, powered by GPT-4V, represents a significant breakthrough in the robotics market. Its ability to seamlessly blend vision and language comprehension, coupled with its adaptability and performance in complex tasks, positions it as a game-changer. Companies in the robotics industry should take note of ViLa’s potential to revolutionize their long-term planning capabilities and open new avenues for innovative applications.