TL;DR:
- VistaLLM, a cutting-edge visual system, revolutionizes vision-language processing.
- It unifies diverse vision-language tasks, enhancing natural language understanding and visual perception.
- Developed collaboratively by top institutions, VistaLLM excels in both coarse and fine-grained tasks across single and multiple input images.
- The model uses an instruction-guided image tokenizer and gradient-aware adaptive sampling for efficient feature extraction.
- Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) evolve to address region-specific vision and language challenges.
- VistaLLM sets new benchmarks in various vision and vision-language tasks, outperforming existing models.
Main AI News:
The era of general-purpose vision systems has been transformed by Large Language Models (LLMs), showcasing their remarkable ability to process visual inputs. This integration has brought together a wide range of vision-language tasks through instruction tuning, marking a significant milestone in the convergence of natural language understanding and visual perception.
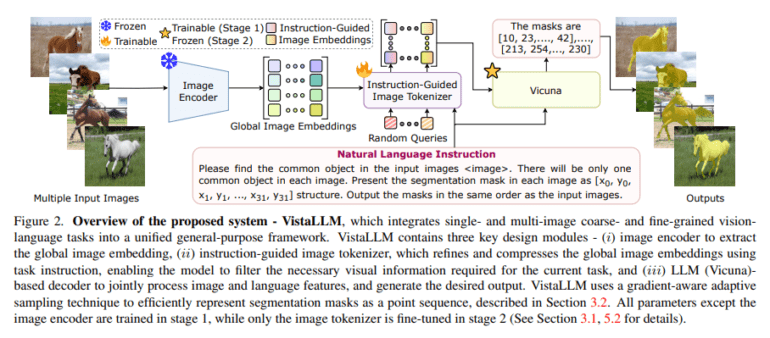
A collaborative effort by researchers from renowned institutions such as Johns Hopkins University, Meta, University of Toronto, and the University of Central Florida has given birth to VistaLLM, a robust visual system that tackles both coarse and fine-grained vision-language tasks across single and multiple input images within a unified framework. Utilizing an instruction-guided image tokenizer and a gradient-aware adaptive sampling technique, VistaLLM efficiently extracts compressed and refined features, representing binary segmentation masks as sequences.
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs), initially designed for image-level tasks such as visual question answering and captioning, have evolved to address region-specific vision and language challenges. Recent advancements, as exemplified by models like KOSMOS-2, VisionLLM, Shikra, GPT4RoI, and Image Encoder Instruction-Guided Image Tokenizer, highlight the integration of region-based referring and grounding tasks within general-purpose vision systems. This progress signifies a significant shift towards enhanced region-level vision-language reasoning, marking a substantial leap in the capabilities of MLLMs for complex multimodal tasks.
While large language models excel in natural language processing, designing general-purpose vision models for zero-shot solutions to diverse vision problems has proven to be a challenge. Existing models need enhancements to effectively integrate varied input-output formats and represent visual features. VistaLLM addresses both coarse- and fine-grained vision-language tasks for single and multiple input images using a unified framework.
VistaLLM stands as an advanced visual system for processing images from single or multiple sources, all within a unified framework. It leverages an instruction-guided image tokenizer to extract refined features and employs a gradient-aware adaptive sampling technique to represent binary segmentation masks as sequences. The study also emphasizes the compatibility of EVA-CLIP with the instruction-guided image tokenizer module in the final model.
Consistently outperforming strong baselines, VistaLLM excels in a broad spectrum of vision and vision-language tasks. It surpasses the general-purpose state-of-the-art on VQAv2 COCO Captioning by 2.3 points and achieves a substantial 10.9 CIDEr points gain over the best baseline. In image captioning, it matches the performance of fine-tuned specialist models, highlighting the language generation capabilities of LLMs. In single-image grounding tasks like REC and RES, VistaLLM also outperforms existing baselines and stands on par with specialist models in RES. Moreover, it sets new state-of-the-art records in diverse studies such as PQA BQA, VCR Novel Tasks, CoSeg, and NLVR, demonstrating its robust comprehension and outstanding performance across various vision-language challenges.
Conclusion:
The emergence of VistaLLM signifies a significant advancement in vision-language processing, offering businesses a powerful tool to excel in a wide range of visual tasks. Its unification of vision-language tasks, efficient feature extraction, and outstanding performance across diverse challenges make it a game-changer in the market, enabling businesses to harness the potential of vision-language integration for enhanced operations and capabilities.