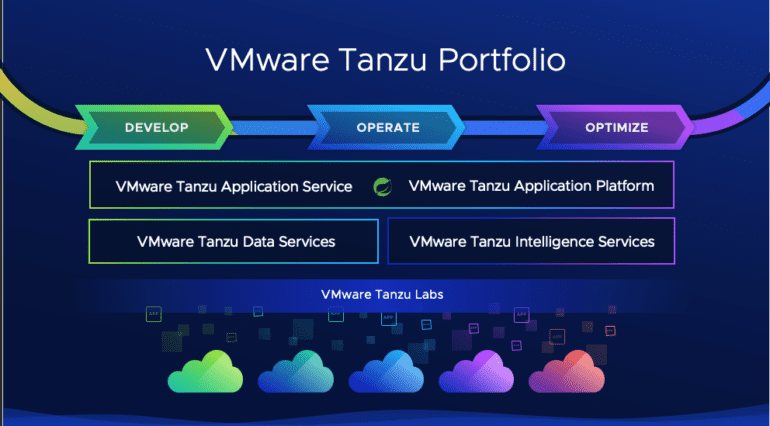
TL;DR:
- VMware introduces a beta Large Language Model (LLM) to enhance its Tanzu platform with AI capabilities.
- Agent software enhancements simplify the deployment of the VMware Tanzu GemFire Vector DB Extension.
- Support for Spring runtime and DORA metrics boosts Java application development.
- Tanzu Hub has a user-friendly interface that integrates with Tanzu Insights and CloudHealth.
- Intelligent Assist in Tanzu is improved for issue diagnosis and resolution.
- New tools: GreenOps for energy tracking, Tanzu Guardrails for governance, and Tanzu Application Catalog for inventory management.
- A technology preview of VMware Tanzu Data Hub streamlines management across cloud and Kubernetes environments.
- Support for Postgres databases and Oracle Cloud VMware Solution extended.
- VMware aims to optimize Kubernetes management, data services, and intelligence services.
- The goal is to enhance the developer experience and simplify cloud-native application deployment.
Main AI News:
VMware, a leader in cloud infrastructure and digital workspace technology, has announced significant advancements in its Tanzu platform, aimed at simplifying and optimizing the application development process. These updates bolster VMware’s commitment to providing developers with a seamless experience and addressing the growing demands of Kubernetes-based environments.
In a bid to harness the power of generative artificial intelligence (AI), VMware has introduced a cutting-edge Large Language Model (LLM) in beta. This LLM, equipped with advanced AI capabilities, is set to revolutionize the Tanzu platform. Alongside this innovation, VMware has extended the functionality of its agent software, integrating machine learning algorithms. These enhancements make it more accessible than ever to deploy the VMware Tanzu GemFire Vector DB Extension, a pivotal tool for expanding the capabilities of LLM-driven applications.
Moreover, VMware has fortified Tanzu’s ecosystem by incorporating support for a Spring runtime tailored to Java applications. This strategic move aligns with the principles of the DevOps Research and Assessment (DORA) framework, introduced by Google. By including metrics like Deployment Frequency and Lead Time for Changes, VMware aims to elevate the efficiency and performance of development processes within the Tanzu environment.
The Tanzu Hub has not been left untouched in this wave of upgrades. It now boasts a revamped user interface, fostering an intuitive and user-friendly experience. Furthermore, the integration of Tanzu Hub with Tanzu Insights and Tanzu CloudHealth empowers users with comprehensive observability and management tools. VMware has also made significant strides in enhancing Intelligent Assist within Tanzu, simplifying the process of diagnosing and resolving issues through seamless access to external resources.
In addition to these improvements, VMware is introducing two groundbreaking tools. The first, GreenOps, is in beta and offers a robust solution for tracking energy consumption, promoting sustainability in cloud-native environments. The second, VMware Tanzu Guardrails, is designed to streamline governance and compliance, ensuring a secure and compliant development landscape.
Recognizing the importance of transparency and inventory management, VMware introduced the VMware Tanzu Application Catalog. This catalog enables organizations to track open source artifacts and provides a comprehensive inventory of software bills of materials (SBOMs).
Taking a step further in simplifying cloud-native management, VMware offers a technology preview of VMware Tanzu Data Hub. This preview promises to streamline the management of VMware Tanzu and data services across various cloud and Kubernetes environments, offering greater control and efficiency.
Notably, VMware has expanded its support for Postgres databases within the Database-as-a-Service (DBaaS) platform for Tanzu. Additionally, it extends support to the Oracle Cloud VMware Solution, enhancing the availability of Kubernetes clusters.
Betty Junod, Vice President of Marketing for the Modern Apps and Management Business Group at VMware, emphasizes VMware’s three-tier approach to managing Kubernetes infrastructure, data services, and intelligence services. This approach is geared towards optimizing the overall development environment, ultimately enhancing the developer experience.
In an era where Kubernetes-based deployments are on the rise, largely due to the proliferation of AI applications, VMware’s holistic approach aims to address the challenges developers face. By centralizing the management of Kubernetes environments, VMware aims to reduce the cognitive load on developers, making it easier to build and deploy cloud-native applications.
While the pace of centralization in Kubernetes management remains uncertain, the growing interest in platform engineering as a methodology for managing DevOps workflows at scale indicates a shifting landscape. The key challenge lies in effectively aligning services with the nature of applications being developed, ensuring that developers have the tools they need to succeed in this dynamic ecosystem.
Conclusion:
VMware’s Tanzu platform enhancements signify a significant step in simplifying and streamlining the application development process. This development aligns with the market’s increasing demand for more efficient and centralized Kubernetes management solutions, especially as AI applications continue to proliferate in cloud-native environments. VMware’s comprehensive approach reflects a commitment to improving the developer experience and underscores the importance of addressing the evolving needs of the market.