- Zyphra introduces Zamba-7B, a compact 7-billion parameter AI model.
- Zamba-7B utilizes the innovative “Mamba/Attention Hybrid” structure for enhanced efficiency and performance.
- Achieves remarkable training efficiency within a short timeframe with minimal computational resources.
- Outperforms competitors like LLaMA-2 7B and OLMo-7B, nearly matching larger models’ performance.
- Zyphra fosters collaboration by releasing Zamba-7B’s training checkpoints under Apache 2.0 license.
- Plans integration with Huggingface and publication of a technical report for the AI community.
Main AI News:
Zyphra’s latest unveiling, the Zamba-7B model, marks a significant leap forward in AI innovation. This compact yet powerful model, boasting 7 billion parameters, not only rivals larger counterparts in performance but also introduces a groundbreaking architectural paradigm aimed at maximizing both efficiency and effectiveness.
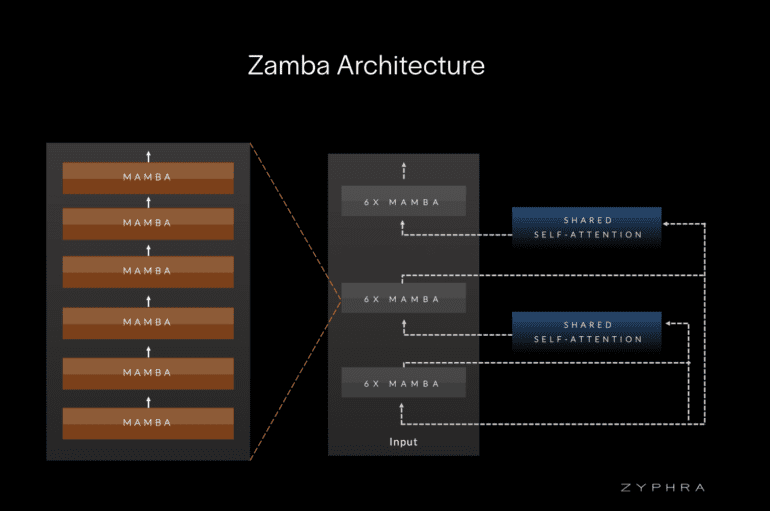
At the heart of the Zamba-7B model lies its revolutionary “Mamba/Attention Hybrid” structure, a brainchild of Zyphra’s expert team. This innovative design marries the efficiency of Mamba blocks with a globally shared attention layer, vastly enhancing the model’s capacity to discern and learn from long-term data dependencies. Deployed strategically every six Mamba blocks, this design optimization minimizes computational overhead, rendering the model highly efficient and pragmatic.
Remarkably, Zamba-7B achieves unparalleled training efficiency, a testament to Zyphra’s prowess. Developed by a lean team of just seven researchers within a mere 30-day timeframe, utilizing 128 H100 GPUs, the model was trained on an extensive dataset of approximately 1 trillion tokens sourced from open web repositories. Leveraging a phased approach, starting with lower-quality data before transitioning to higher-quality sets, not only elevates performance but also streamlines computational requirements.
In comparative assessments, Zamba-7B outshines competitors like LLaMA-2 7B and OLMo-7B, nearly matching the performance of larger counterparts such as Mistral-7B and Gemma-7B while consuming fewer data tokens, underscoring its design efficiency.
Zyphra’s commitment to fostering collaboration within the AI research community is evident in its decision to release all Zamba-7B training checkpoints under the Apache 2.0 license. The model’s open-source nature, combined with its stellar performance and efficiency, positions it as a game-changer in the AI landscape. Zyphra further plans to integrate Zamba with Huggingface and publish a comprehensive technical report, empowering the AI community to leverage and extend their innovations effectively.
The emergence of models like Zamba-7B signifies a pivotal moment in AI advancement, championing not only performance excellence but also sustainability and accessibility. By demonstrating the potential for superior performance with fewer resources, these models set the stage for a more eco-friendly and resource-efficient approach to AI development.
Conclusion:
Zyphra’s Zamba-7B marks a significant advancement in AI technology, redefining efficiency and performance benchmarks. Its compact size, coupled with groundbreaking architectural innovations, not only outperforms competitors but also sets a precedent for collaborative development in the AI market. This signals a shift towards more sustainable and accessible AI technologies, reshaping the landscape for future innovations.