TL;DR:
- Google merges Mandiant and Chronicle into Google Cloud Security AI Workbench.
- The workbench features a generative AI chatbot for code analysis and conversations.
- Users gain insights into system vulnerabilities and prevention methods.
- Google collaborates with DeepMind to develop the chatbot and refocus AI efforts.
- Breach alerts from Mandiant and security data from Chronicle are accessible.
- Accenture becomes the first partner, with more expected to join in the future.
- AI-assisted code checking and creation is a growing concept.
- The human programmer retains control, but AI offers valuable assistance.
- The market may shift towards employing AI for security code implementation.
Main AI News:
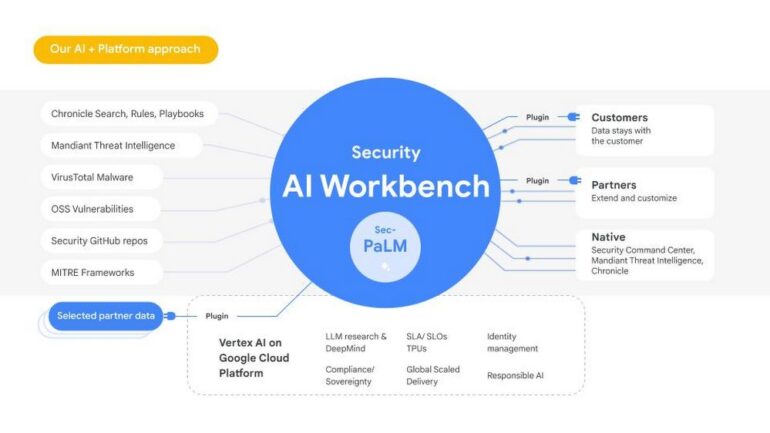
Google’s foray into cybersecurity has been marked by the launch of several notable operations in recent years. Two significant endeavors, Mandiant and Chronicle, will now merge with other services under a new comprehensive platform called Google Cloud Security AI Workbench. Embodying the style and prowess of a business magazine, this unified platform introduces a groundbreaking generative AI chatbot reminiscent of ChatGPT, leveraging a customized version of Google’s PaLM model tailored for security purposes. Users can conveniently submit lines of code for analysis while engaging in conversations with the chatbot, free from the shackles of specialized jargon. The chatbot imparts valuable insights into potential system vulnerabilities, enlightening users on the methods hackers employ and offering effective strategies to preempt or repel such threats.
During RSAC 2023, Sunil Potti, the Vice President and General Manager of Security at Google Cloud, unveiled the Security AI Workbench as an amalgamation of Mandiant and Google’s threat intelligence data. By integrating these extensive datasets into a single enterprise-grade platform, Google has birthed an unprecedented security large language model (LLM), an industry first. This remarkable creation, encased within the Security AI Workbench, aims to fortify the realm of generative AI while exceeding the confines of a mere product.
DeepMind, a subsidiary of Google, collaborated closely in the development of this revolutionary chatbot. This collaboration signifies a broader initiative within Google, where DeepMind and the Google Brain team have embarked on a unified pursuit, steering the trajectory of the company’s artificial intelligence endeavors.
Sunil Potti expressed his team’s ambition, stating, “We continuously prioritize security measures to safeguard our consumer space and enterprise clientele. We pondered whether we could pioneer applicability in the domain of generative AI that transcends the realm of a mere product.” These profound words were conveyed to The Wall Street Journal, accentuating the significance of this ambitious undertaking.
Complementing the generative AI system, users gain access to breach alerts from Mandiant and a vast library of security data housed within Chronicle. This unified interface empowers users to monitor and address security concerns from a single comprehensive dashboard. Additionally, it is expected that Google will augment the workbench with further cybersecurity applications in the foreseeable future, bolstering its appeal and utility.
Google adopts a collaborative approach, inviting partners to contribute to the development and refinement of its AI system. Accepted firms are granted the privilege of uploading code, thus enhancing the system’s detection and generative capabilities. Accenture, a renowned industry player, stands as the inaugural partner to join forces with Google at the launch of this groundbreaking initiative, and Sunil Potti anticipates the inclusion of other influential entities during the upcoming summer.
The notion of an AI scrutinizing and generating code remains an unfamiliar concept for many. However, early reports from OpenAI and Google indicate promising results. The present value proposition highlights the AI’s potential to serve as an invaluable assistant, proficiently parsing code, detecting errors, and offering alternative solutions. Nevertheless, it is crucial to emphasize that the human programmer retains ultimate authority over the entire process.
The question of whether this power dynamic will persist for five years looms large, particularly in light of the current talent-demand disparity across various programming sectors, notably in cybersecurity and cloud domains. Businesses may increasingly consider the adoption of AI over specialized professionals, entrusting general or low-code technicians to implement security measures using AI-driven services.
Conlcusion:
Google’s introduction of the Google Cloud Security AI Workbench represents a significant leap forward in the cybersecurity market. By integrating Mandiant and Chronicle into a unified platform, bolstered by a generative AI chatbot, Google empowers users with advanced code analysis and dialogue capabilities. This collaboration with DeepMind further emphasizes Google’s commitment to artificial intelligence.
With the potential for additional cybersecurity applications and the invitation for partners to enhance the system, Google’s workbench sets the stage for transformative advancements. As the market evolves, the use of AI for code implementation may gain traction, providing businesses with more efficient security practices and the ability to tap into a broader pool of technical resources.