- Google DeepMind’s SIMA Project pioneers AI advancements in dynamic 3D environments.
- Integration of visual perception and language processing enables human-like task execution.
- Traditional AI models struggle in dynamic spaces, highlighting the need for adaptable systems.
- SIMA introduces a novel approach leveraging machine learning and extensive datasets.
- Agents trained to process language and visual data for adept navigation and interaction.
- Empirical evaluations showcase enhanced performance in real-world task execution.
- SIMA agents demonstrate adaptability and proficiency across diverse virtual environments.
Main AI News:
The quest to maximize artificial intelligence efficacy within dynamic 3D realms has become a pivotal research endeavor, seeking to bridge the chasm between static AI models and practical real-world applications. Google DeepMind has spearheaded this frontier, pioneering sophisticated agents adept at interpreting and executing intricate directives across diverse simulated landscapes. This groundbreaking AI initiative transcends traditional paradigms by seamlessly integrating visual perception with language processing, enabling AI systems to undertake human-like tasks in multifarious virtual environments.
A critical challenge in this domain lies in the inherent limitations of AI agents to dynamically engage within three-dimensional spaces. Conventional AI architectures excel in environments with well-defined, static tasks and responses but flounder when confronted with environments characterized by continual flux and multifaceted objectives. This glaring disparity underscores the imperative for a robust system capable of adapting and responding to unpredictable scenarios, mirroring real-world interactions.
Historically, prevailing methodologies have leaned on rigid command-response frameworks, confining AI agents to a narrow spectrum of predictable, controlled actions. However, such frameworks fail to facilitate the generalization of learned behaviors across new or evolving contexts, particularly in scenarios necessitating real-time decision-making and adaptability. Hence, there’s a pressing need for more versatile and dynamic AI capabilities.
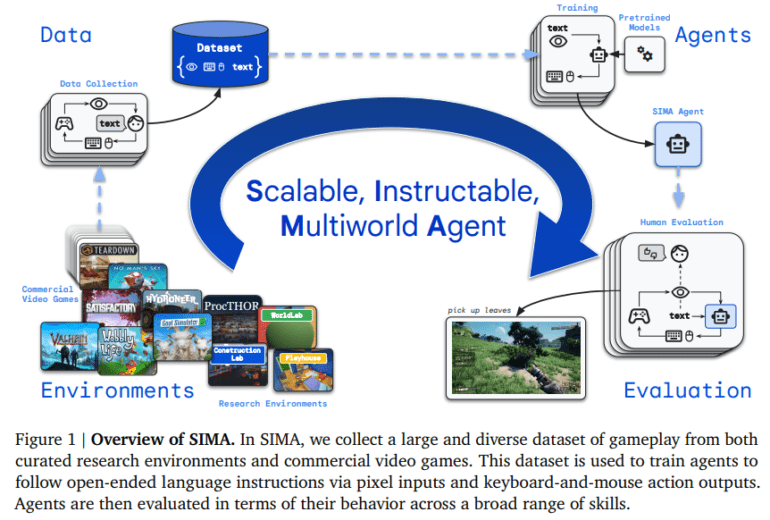
Enter the SIMA (Scalable, Instructable Multiworld Agent) project, a collaborative endeavor between Google DeepMind and the University of British Columbia, poised to surmount these challenges. The SIMA framework pioneers a novel approach that amalgamates advanced machine learning models with extensive datasets to cultivate agents proficient in comprehending and executing diverse instructions. By amalgamating language directives with sensory input from 3D environments, SIMA agents exhibit prowess in executing complex tasks necessitating cognitive acumen and physical interactions.
At the heart of SIMA lies a methodology centered on training agents to seamlessly process amalgamated inputs of language and visual data, empowering them to navigate and interact adeptly within virtual landscapes. These landscapes span meticulously crafted simulation platforms to open-ended video games, offering agents a rich tapestry of tasks and scenarios to navigate. Through the utilization of pretrained neural networks coupled with continuous learning mechanisms, SIMA agents adeptly generalize their competencies across disparate settings, effectively bridging the gap between specific directives and tangible actions within digital realms.
Empirical assessments of SIMA agents underscore their heightened aptitude in interpreting and executing diverse instructions. Performance evaluations conducted across varied platforms unveil remarkable achievements in executing tasks mirroring real-world activities, encompassing navigation, object manipulation, and intricate problem-solving. Notably, in a comprehensive evaluation, SIMA agents exhibited an impressive task completion rate of 75% across multiple video games, underscoring their adaptability and proficiency across diverse virtual environments and challenges.
Conclusion:
Google DeepMind’s SIMA Project signifies a monumental leap in AI capabilities, particularly within dynamic 3D realms. By seamlessly integrating visual perception with language processing, SIMA agents exhibit remarkable adaptability and proficiency in executing human-like tasks across diverse virtual landscapes. This innovation heralds a new era of AI dynamics, promising transformative implications for industries reliant on AI-driven solutions. Companies leveraging such advancements stand poised to gain a competitive edge by harnessing AI systems capable of navigating complex, ever-changing environments with unparalleled efficacy.